Key Findings:
- The U.S. restaurant and foodservice industry is forecasted to reach $1.5 trillion in sales in 2025 — a 4% increase versus 2024.
- This growth underscores its role as a key economic driver, accounting for approximately 4% of GDP.
- The projected 2025 revenue also represents a 74% growth from 2019.
- There are over 1 million restaurant and foodservice establishments across the country.
- The industry is projected to add around 200,000 new jobs in 2025, driving total employment to 15.9 million.
- Full-service restaurants currently have an average profit margin of around 9.8%.
- About 65% of consumers prefer off-premises dining through drive-thru or pickup options.
- The state with the highest concentration of restaurants is California: home to nearly 10% of all restaurant locations in the country.
- When it comes to cities with the largest number of restaurants, New York City has close to 18,000 dining establishments.
The restaurant industry in the United States is achieving new milestones, with a gradually rebounding workforce and record-high spending. However, operators continue to face challenges such as rising food costs, labor shortages and shifting consumer preferences.
That’s why we’ve compiled the most important U.S. restaurant industry statistics for 2025. Below, we’ll discuss revenue, employment, consumer behavior and other numbers shaping the industry.
Whether you’re simply seeking data or looking to benchmark your business, these insights help reveal where the industry stands and where it’s headed.
Industry Overview: Size and Economic Impact
In 2025, the restaurant industry continues to be a vital component of the U.S. economy, contributing significantly to GDP and providing employment to millions.
Market size & GDP contribution
The country’s restaurant and foodservice industry is expected to reach $1.5 trillion in sales this year — a 4% increase compared to 2024, indicating strong consumer demand and industry growth.

This substantial figure underscores the industry’s critical role as a driver of the U.S. economy, accounting for approximately 4% of GDP.
It’s also worth noting that there are currently over 1 million restaurant and foodservice outlets nationwide.
Beyond its economic contributions, the industry plays a significant cultural role, serving as a cornerstone for social gatherings and community engagement.
Revenue and Sales Trends
The industry has shown remarkable resilience and growth, with sales figures reaching impressive heights. .
Record sales in 2024–2025
Traditional restaurant sales — encompassing full-service, limited-service, and bar and tavern segments — are expected to surpass $1.1 trillion in 2025, marking a 4.1% year-over-year increase.
This growth trajectory reflects the industry’s robust recovery from the pandemic and its ability to meet pent-up consumer demand.
Growth drivers
Several factors contribute to this growth, including inflation-adjusted increases in consumer dining expenditures, technological innovations enhancing customer experiences and a strong preference for dining out.
However, it’s important to note that rising menu prices, driven by increased food and operational costs, also play a role in the overall revenue growth.
Historical comparison
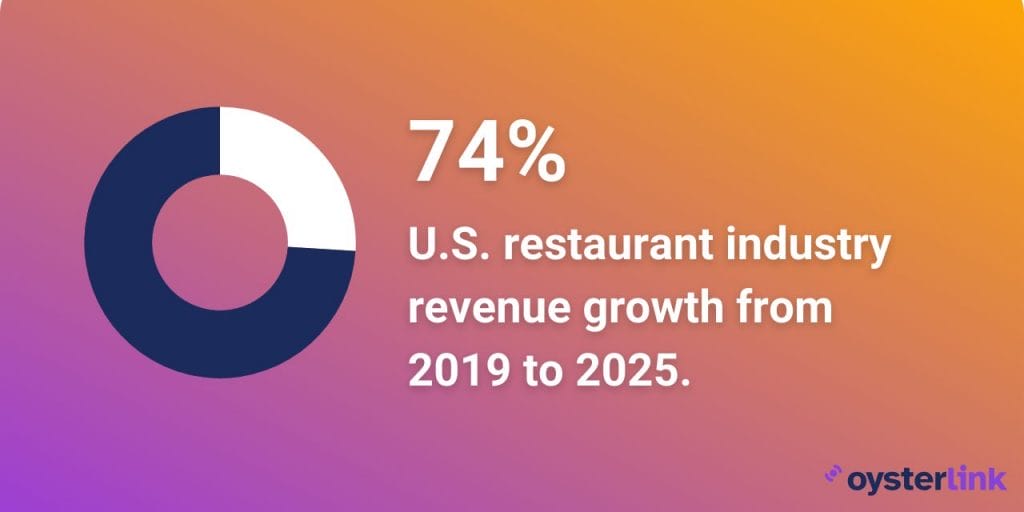
Compared to the 2019 revenue of approximately $864 billion, the 2025 projections indicate a significant upward trajectory, demonstrating the industry’s resilience and capacity for recovery despite economic challenges.
The projected 2025 revenue represents a 74% growth from pre-pandemic levels — underscoring not just recovery, but robust expansion driven by evolving consumer habits, widespread digital adoption and strong market demand.
Profit margins
The average profit margin for full-service restaurants stands at around 9.8% in 2025. While this reflects relative stability and recovery from pandemic-related lows, profit margins remain under pressure due to significant operational costs.
Rising food prices, labor costs, rent increases and supply-chain disruptions have notably impacted margins across the sector. For instance, food prices alone increased approximately 6.2% year-over-year in early 2025, forcing many restaurants to raise menu prices to maintain profitability.
Additionally, the ongoing labor shortage has compelled operators to increase wages substantially, further squeezing profitability.
Despite these challenges, restaurant operators are employing various strategies to protect profit margins. Examples include:
- Menu optimization
- Reducing ingredient complexity
- Adopting digital solutions to streamline ordering and inventory management
- Investing in automation to offset labor costs
Segment-wise Revenue Breakdown
The U.S. restaurant industry in 2025 exhibits diverse performance across its various segments, reflecting consumer preferences and market dynamics.
Full-service restaurants
Full-service restaurants, characterized by table service and a comprehensive menu, have experienced steady growth.
As of 2025, the market size for single-location full-service restaurants is approximately $253.9 billion, with an annual growth rate of 9.2% between 2020 and 2025. (Source)
Quick-service restaurants (QSRs)
Quick-service restaurants, commonly known as fast-food establishments, continue to dominate the market.
The QSR segment has seen a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 0.26% in recent years, driven by factors such as digital ordering and accessibility. (Source)
Fast-casual restaurants
Known for providing higher-quality food and a better dining experience than traditional fast-food establishments, this restaurant category continues experiencing robust growth in 2025.
The U.S. fast-casual market is projected to grow significantly, adding approximately $84.5 billion in revenue between 2025 and 2029, with a CAGR of 13.7%. (Source)
This accelerated growth is largely driven by increased consumer demand for convenience combined with quality and menu innovation.
Key players, such as Chipotle, Shake Shack and Cava, have notably expanded their footprints due to strong brand positioning and digital adoption strategies.
Bars and taverns
Bars and taverns have seen a resurgence as social venues, contributing notably to the industry’s revenue.
Revenue for bars, nightclubs, and taverns in the U.S. has reached approximately $36.9 billion in 2025, marking a 2.5% increase over the previous year.
Profit margins within this segment have stabilized at around 9%, demonstrating effective adaptation to consumer trends and inflation pressures. (Source)
Employment and Workforce Statistics
The restaurant industry’s workforce dynamics in 2025 reflect both growth and ongoing challenges.
Industry employment levels
As the second-largest private-sector employer, the industry is projected to add approximately 200,000 new jobs in 2025, bringing total employment to 15.9 million.

This highlights the industry’s role in providing diverse employment opportunities across the nation.
Workforce composition
The restaurant workforce remains highly diverse, reflecting the industry’s longstanding role as a gateway employer for younger workers and various cultural communities.
Around 47% of restaurant employees are minorities, well above the average across other industries.
Additionally, younger workers aged 16 to 34 represent nearly two-thirds of the workforce, highlighting the industry’s role in providing initial employment experiences for younger demographics.
Labor shortages & turnover
Despite employment growth, the industry continues to face significant workforce challenges, including high vacancy rates and turnover exceeding 70%.
High turnover remains a major problem, particularly in quick-service and casual dining segments, where staffing instability directly impacts operational efficiency, service quality and customer satisfaction.
These labor shortages have been exacerbated by intense competition from other sectors, including retail and logistics, which have similarly increased wages and benefits to attract workers.
Additionally, evolving employee expectations regarding better wages, flexible scheduling and improved working conditions have made recruitment and retention increasingly difficult.
Lastly, changing demographics and workforce attitudes — particularly among younger workers (Gen Z) — highlight a shift toward prioritizing workplace culture, flexibility and professional growth opportunities.
Restaurants responding effectively to these expectations, such as by offering clearer advancement paths and investing in employee training, have seen improved retention rates.
Consumer Spending and Behavior Trends
Understanding consumer behavior is crucial for assessing the U.S. restaurant industry’s performance in 2025.
Note: This report on U.S. restaurant industry statistics for 2025 focuses mostly on hard data. For insights on broader shifts like technology and new dining habits, check out our Restaurant Industry Trends guide.
Average spend per visit
Economic factors have influenced consumer spending patterns. As of January 2025, U.S. restaurant sales reached $98.6 billion, marking a 5.4% increase from the previous year.
However, after adjusting for rising menu prices, the real growth in restaurant spending was 2%.
This indicates that while consumers are spending more, a portion of this increase is attributed to inflation rather than increased consumption.
Dining frequency and preferences
Consumer dining habits have evolved significantly. Approximately 65% of consumers prefer ordering food through drive-thru or pickup options over dining in person.
This shift towards off-premises dining highlights convenience as a top priority.
Additionally, 51% of diners turn to restaurant apps to discover deals and discounts that could offset their expenses. This shows that cost-conscious ordering is a priority, as consumers actively seek ways to save while enjoying restaurant meals.
Not to mention, recent government data predicts a 3.4% increase in prices for food consumed away from home (i.e., at restaurants).
Regional Insights and Variations
Restaurant industry performance in 2025 also varies significantly by region, reflecting different economic conditions and demographics across the U.S.
Leading states by restaurant growth
States such as Florida and Texas have seen remarkable restaurant-sector growth, benefiting from robust population increases, strong local economies and favorable regulatory environments.
For instance, Florida alone is projected to generate $73.9 billion in restaurant sales in 2025, driven by its rapidly growing population and thriving tourism sector.
Texas similarly continues to experience substantial industry expansion, supported by consistent population influx and lower operational costs.
Highest restaurant density
In terms of restaurant density, California and New York lead the nation. In fact, California alone accounts for nearly 10% of all restaurant locations nationwide.
Despite challenges like high minimum wage requirements and regulatory complexities, California’s restaurant industry continues to thrive due to its large consumer base, diverse food culture and tourist appeal.
Meanwhile, New York City boasts one of the highest restaurant densities in the U.S., with nearly 18,000 restaurants, reflecting a strong culinary culture despite ongoing economic pressures and high competition.
Regional wage and employment variations
Regional differences in restaurant wages remain significant, affecting labor dynamics across the industry.
For instance, California’s average hourly wage for restaurant workers reached approximately $19.50 per hour in 2025, driven by statewide minimum wage laws and intense competition for workers.
In contrast, Southern states like Georgia and Alabama typically exhibit lower average wages, around $15 per hour, reflecting different living costs and competitive dynamics.
Find and apply for restaurant jobs
Regional Consumer Preferences
Consumer dining preferences vary regionally as well. The West Coast, particularly California and Oregon, continues to lead the nation in sustainable and plant-based dining demand.
In contrast, the Southeast and Midwest regions prioritize affordability, convenience and comfort-focused dining options — fueling growth in quick-service and fast-casual segments.
Meanwhile, the Northeast remains a stronghold for premium dining experiences, craft cocktail bars and innovative restaurant concepts.
These regional differences underscore the importance of understanding localized economic conditions, demographics and consumer behaviors for accurately assessing the U.S. restaurant industry’s overall landscape in 2025.
FAQs About U.S. Restaurant Industry Statistics
The U.S. restaurant and foodservice industry is projected to reach $1.5 trillion in sales in 2025, marking a 4% increase from 2024. Additionally, it accounts for approximately 4% of GDP.
As of 2025, there are over 1 million restaurant and foodservice establishments across the country. These range from full-service and fast-casual to quick-service restaurants, bars and taverns.
Fast-casual restaurants are experiencing the fastest growth, projected to add $84.5 billion in revenue between 2025 and 2029, driven by consumer preferences for convenience combined with higher-quality offerings and digital services.
Texas and Florida are leading in job creation within the restaurant sector, each adding over 10,000 new restaurant jobs in 2025, representing a 4% increase in employment from the previous year.
New York City has one of the highest restaurant densities, with nearly 18,000 establishments across its five boroughs. Despite economic challenges, NYC maintains its robust dining scene driven by local demand and tourism.




