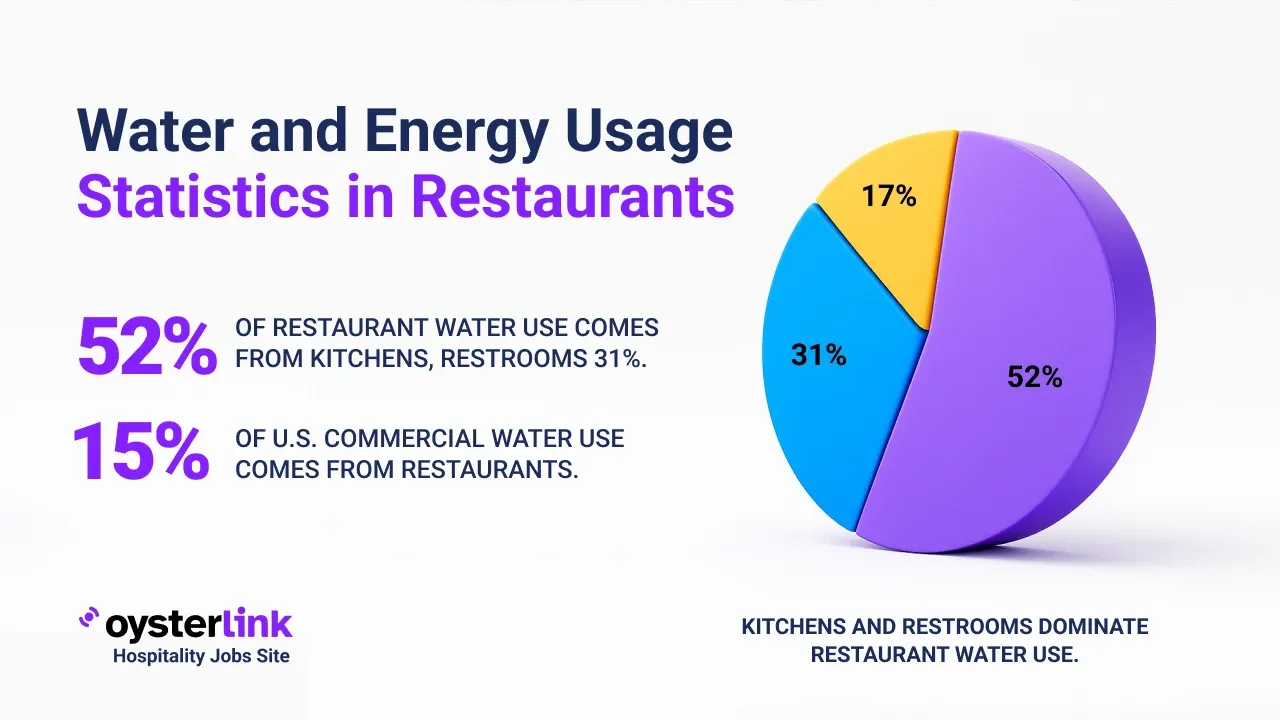
San Diego Living Wage vs Cashier Salary: Key Takeaways
- San Diego's minimum wage increased to $17.25/hour as of January 1, 2025, above California's state minimum of $16.50/hour.
- The average cashier salary in San Diego is $19.29/hour, about $40,123 annually for full-time work.
- The MIT Living Wage Calculator estimates a needed wage of $30.71/hour ($63,876 annually) for a single adult to cover basic living expenses in San Diego.
- High housing costs—median home price of $910,000 and average rent $3,175/month—are key drivers of the wage-to-living cost gap.
Understanding how cashier salaries compare with the living wage in San Diego is essential given the region's high cost of living.
This article explores the wage disparity and strategies to bridge the gap for cashier workers.
For employers looking to attract and retain prominent talent, how to hire a cashier offers valuable insights tailored to the unique challenges of this position.
1. San Diego Living Wage and Cashier Salary Overview
San Diego raised its minimum wage to $17.25 per hour effective January 1, 2025, outpacing California's state minimum wage of $16.50 per hour. This makes San Diego one of the cities with a higher baseline wage to better address local expenses.
Cashiers in the area earn considerably more than the minimum wage, with average hourly wages estimated at $19.29. This equates to about $40,123 per year assuming a 40-hour workweek and full-year employment.
While this may seem like a decent hourly rate, when juxtaposed with the high cost of living in San Diego, this salary presents challenges for many workers.
For individuals considering a career as a cashier, understanding the cashier job description can provide clarity on roles and expectations in this position.
2. Cost of Living in San Diego and Impact on Cashiers
According to the MIT Living Wage Calculator, a single adult in San Diego needs to earn roughly $30.71 per hour to cover basic needs such as housing, food, transportation, and healthcare. This adds up to an annual income requirement of $63,876, well above both the minimum wage and average cashier salary.
The disparity mainly arises from San Diego's high housing costs. The city's median home price stands at about $910,000, ranking as the fourth most expensive among the 30 largest U.S. cities. Moreover, the average monthly rent has climbed to $3,175, making it the third-highest national average.
These housing expenses heavily influence the living wage calculation and create a difficult economic environment for cashiers, who represent a significant portion of entry-level workers in the retail sector.
Employers interested in effective hiring practices amidst San Diego's unique labor market conditions should explore restaurant staff hiring strategies which can be adapted to other hospitality roles including cashier positions.
Housing Costs Driving Wage Gap
Housing affordability remains the largest obstacle for low-to-moderate income earners in San Diego. Cashier wages have struggled to keep pace with skyrocketing rents and home prices.
This gap forces many workers to allocate a disproportional share of income to housing, compromising their ability to afford other essentials.
3. Strategies to Bridge San Diego Wage Gap for Cashiers
Addressing the gap between cashier earnings and the living wage in San Diego requires a multifaceted approach.
Wage Adjustments
Increasing cashier wages beyond current averages could provide immediate relief. Employers can examine their pay scales and consider raising hourly rates to a level closer to the living wage.
For hiring managers, understanding best practices in compensation and benefits can be assisted by resources such as posting jobs with salary tips to attract suitable candidates.
Cost-of-Living Adjustments (COLAs)
Regular COLAs aligned with inflation and housing cost trends can help wages sustain purchasing power over time. Implementing COLAs ensures that employees’ earnings do not erode as living expenses climb.
Housing Assistance Programs
Expanding access to affordable housing initiatives is vital. Government subsidies, employer-sponsored housing benefits, or partnerships with housing organizations could reduce the financial burden on cashiers.
Skill Development and Career Advancement
Investing in cashier skill development can open pathways to higher-paying roles within retail or related industries. Training programs and education support can promote career growth and better income opportunities.
Cashiers aspiring to improve their careers can learn more about interview preparation in our cashier interview questions guide.
4. Conclusion: San Diego Living Wage vs Cashier Salary
The disparity between the average cashier salary and the living wage reflects broader economic challenges facing many workers in San Diego.
While the city has raised its minimum wage above the state level, the high cost of living, especially housing expenses, means many cashiers still struggle to meet basic needs.
Employers, policymakers, and community organizations must work collaboratively to develop solutions such as wage increases, cost-of-living adjustments, affordable housing programs, and career development opportunities to bridge this gap.
Ensuring competitive wages and sustainable working conditions is critical for attracting dependable cashier staff, as emphasized in how to hire a cashier.
These actions are essential to promote economic stability and quality of life for San Diego’s retail workforce.
5. Useful Resources for San Diego Living Wage and Employment
- California Department of Industrial Relations: Minimum Wage Information
- City of San Diego Official Website
- U.S. Department of Labor: Wage and Hour Division

.webp)
.webp)