Virtual Reality in Bartending: Key Takeaways
- VR Bartending training replaces traditional methods by offering immersive digital practice without real-world risks.
- Training includes modules on drink recipes, pouring techniques, inventory management and customer interaction.
- Trainees receive immediate feedback and performance scores via VR platforms, aiding faster learning and retention.
- VR can reduce training costs and ingredient waste with a large return on investment (ROI) possible after initial hardware setup.
VR training is set to add $294 billion to the global economy by 2030, highlighting its transformative impact across sectors like hospitality and education. In hospitality, training staff quickly and safely remains a challenge.
Traditional bartending courses require costly ingredients, supervision and real customer interaction, which can be stressful and expensive. VR offers a modern solution, enabling trainees to develop essential skills in realistic digital environments without risks or costs.
This article explores how VR works for Bartender training, its benefits, costs, drawbacks and future prospects.
How Virtual Reality Is Used in Bartending Training
VR is a technology that immerses users in a simulated environment using headsets and motion controllers.
In Bartending training, VR allows trainees to practice mixing drinks, restocking and handling customer interactions in realistic virtual bars — without any actual alcohol or supplies. This setup uses sensors and software to create diverse scenarios, helping learners build confidence and skills safely and efficiently.
Software platforms provide different scenarios, ranging from quiet cocktail lounges to high-volume nightclubs. Some VR platforms can also integrate trainee data and results into existing learning management systems (LMS) or staff management systems — a bonus for bar owners juggling multiple locations or tracking progress across a team.
Trainees might find themselves behind the bar mixing drinks, restocking virtual shelves or diffusing a virtual customer dispute. These digital environments are designed to resemble real work settings as closely as possible, providing a safe space to make (and learn from) mistakes.
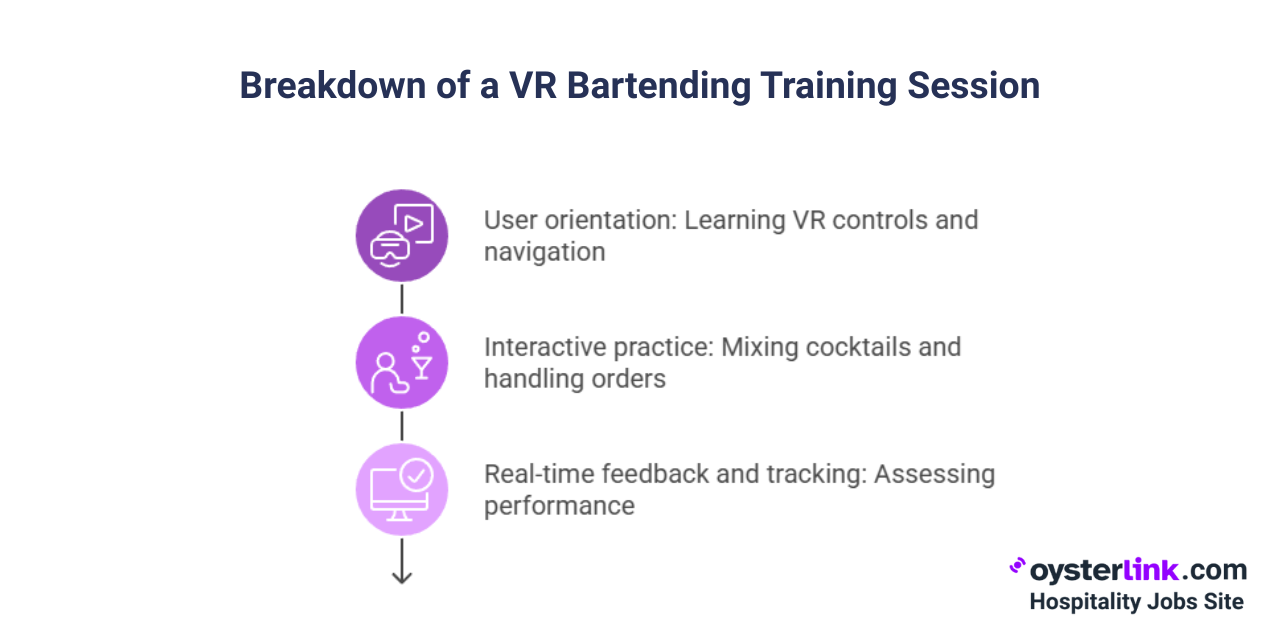
Breakdown of a VR Bartending Training Session
A typical VR bartending training session is structured to gradually build skills, combining orientation, practical exercises and feedback. Here's a closer look at the key stages:
User orientation
A typical VR Bartender training session starts with user orientation — learning how to use controllers, adjust headset fit and navigate the virtual space. Trainees usually complete guided modules covering classic bar setup, drink recipes, proper pour techniques and clean-up routines.
Interactive practice
Once oriented, trainees jump into interactive tasks: mixing classic cocktails, handling multiple orders when things get hectic and interacting with simulated customers (including the odd difficult guest or last-minute order).
Sessions typically last 30–60 minutes but can be shortened or lengthened for flexibility — a helpful feature for trainers working around odd shift patterns or event nights.
Real-time feedback and tracking
The software tracks every step, giving trainees scores and immediate feedback on accuracy, efficiency and customer service. For busy operators, this means less hands-on supervision and more targeted coaching only where needed.
Skills Gained Through VR Bartending Training
VR bartending training helps develop a range of essential skills in a realistic, risk-free environment. The key competencies include:
- Mixing techniques: Practicing precise pours, shaking, stirring and garnishing with virtual ingredients (repeatability saves actual inventory).
- Customer service: Simulated guests test how Bartenders adapt to Gen Z clientele, traditional regulars and unexpected scenarios — ideal for teaching soft skills under pressure.
- Inventory management: Learning how to track stock levels, restock shelves and handle shortages.
Each skill is assessed in real time. For example, VR systems can analyze the accuracy of a pour or how a Bartender responds to an upset customer, highlighting specific areas for improvement and allowing individualized coaching for new hires or students.
In one training session, a new hire might get flagged for handling an impatient guest too robotically, leading to a bit of real-world coaching afterward.
Advantages of VR in Bartending Training
Switching to VR bartending training offers several key benefits over traditional methods, making it an attractive option for modernizing onboarding and attracting younger staff. Here are some of the main advantages:
- Cost and resource efficiency: VR means no more wasted ingredients or broken glassware during practice. Bars and schools save money on supplies and can reuse the same hardware for countless trainees. After the initial setup, most recurring costs are limited to software licensing or hardware upgrades.
- Training time reduction and scalability: Olivia Bistro is a great example of VR’s impact, reducing training duration from 30–40 hours down to just 3–6 hours. Over the course of a year, they trained 100 employees using VR, demonstrating how this technology can greatly accelerate onboarding and efficiently support large-scale staff training.
- Performance improvement: Studies indicate VR training can boost employee performance by 40%, resulting in quicker mastery, better customer interactions and more consistent quality. VR’s ability to provide real-time analytics and personalized feedback accelerates learning effectively.
- Enhanced realism and engagement: VR immerses users in authentic environments, leading to faster learning and higher retention compared to passive methods like videos or manuals. Gamification elements — such as earning badges or competing — also significantly increase engagement, especially among Gen Z and millennial staff.
- Immediate feedback and performance tracking: VR systems monitor every move and provide instant insights, allowing managers to personalize coaching, identify top talents quickly and reduce mistakes early in the training process.
Challenges and Limitations of VR Bartending Training
Despite its many benefits, VR training does have hurdles. These include:
- Technical barriers: Quality VR setups can cost $800–$2,000 or more and require powerful computers or consoles. Some users may experience discomfort or motion sickness. It’s wise to try different headsets and consider group licensing or bundle deals to manage costs.
- Limited sensory simulation: Current VR systems can't replicate the tactile feel of a chilled glass or the aroma of garnishes. Skills reliant on taste and smell still require traditional practice. Hybrid approaches — VR for technique and live for sensory skills — are most effective.
- Industry adoption: While large chains and upscale bars are adopting VR, smaller businesses may remain cautious. Costs are decreasing, making it more accessible, but some skepticism remains. Owners can host trial days or small competitions to showcase VR’s benefits and build team buy-in.
The Future of VR in Bartending Education
VR is rapidly advancing, with new innovations making virtual training even more realistic and better integrated into hospitality workflows. Some exciting developments on the horizon include:
- Haptic gloves and advanced sensors that simulate tactile feedback, allowing users to feel the weight and texture of objects.
- AI-powered customization for guest interactions, regional drinks and adaptive difficulty levels tailored to each trainee.
- Mobile dashboards and remote coaching that would allow Managers to monitor progress, assign modules and give guidance from anywhere — ideal for busy operators with multiple locations.
Collaborations between technology providers and industry leaders are accelerating these improvements, paving the way for highly realistic, accessible and scalable training solutions.
Keep an eye on industry beta tests and pilot programs — they’re often opportunities to get an early foothold.
Long-term impacts and standards
As VR gains acceptance, it could redefine global standards in Bartender training. Certification bodies may begin recognizing VR modules as official components of skills assessments, ensuring consistent quality worldwide.
This democratization of high-quality training can uplift standards at independent venues and chains alike, fostering a more skilled and diverse workforce.
Popular VR Training Providers and Tools
As the industry adopts VR more widely, several top platforms and tools stand out:
- Bartender VR Simulator: Offers realistic scenarios for drink mixing and customer service — aimed at both beginners and pros.
- Two Reality & Bacardi Training Application: An interactive VR app developed with Bacardi, designed to enhance practical skills through engaging, gamified experiences.
- Diageo Bar Academy: Provides comprehensive online and VR modules focused on bartending skills, brand knowledge and industry insights.
- The Mixologist: A multiplayer social VR game that allows players to collaborate, compete and practice in a fun virtual bar environment, fostering team building and skill development in a relaxed setting.
Watch the video below to see "The Mixologist" VR game in action.
Practical Tips for Implementing VR in Your Venue
Here are some useful tips to help you effectively integrate VR training into your venue:
- Request demos or trial periods from VR providers before making purchases.
- Collaborate with local hospitality colleges or bar networks to share platforms and reduce costs.
- Use VR competitions and showcases to familiarize staff and boost enthusiasm.
- Stay connected with user communities for tips, updates and troubleshooting advice.
- Combine VR training with traditional hands-on practice to ensure comprehensive skill development and higher staff satisfaction.