Nevada Labor Law Guide
A comprehensive guide to Nevada labor laws: Covering key topics including minimum wage regulations, overtime provisions, mandated breaks, hiring and termination procedures and other miscellaneous employment laws.
Key Takeaways
- The minimum wage in Nevada for all employees is $12 per hour
- Employees should get paid 1.5 times their usual hourly rate any time they have worked over 40 hours in a week
- In Nevada, eligible employees can take up to 12 weeks of unpaid leave with job protection, following the federal Family and Medical Leave Act (FMLA)
- Employees are required to allow at least a 30-minute break for every eight straight hours of work
- In Nevada, minors aged 14 and older are not required to have a work permit
- Nevada aligns with Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) standards for workplace safety
Minimum Wage Regulations in Nevada
Nevada has its own minimum wage rates that are above the federal minimum wage.
Regular Employees
At the beginning of the year 2024, the minimum wage in Nevada increased to its historical maximum of $12.00.
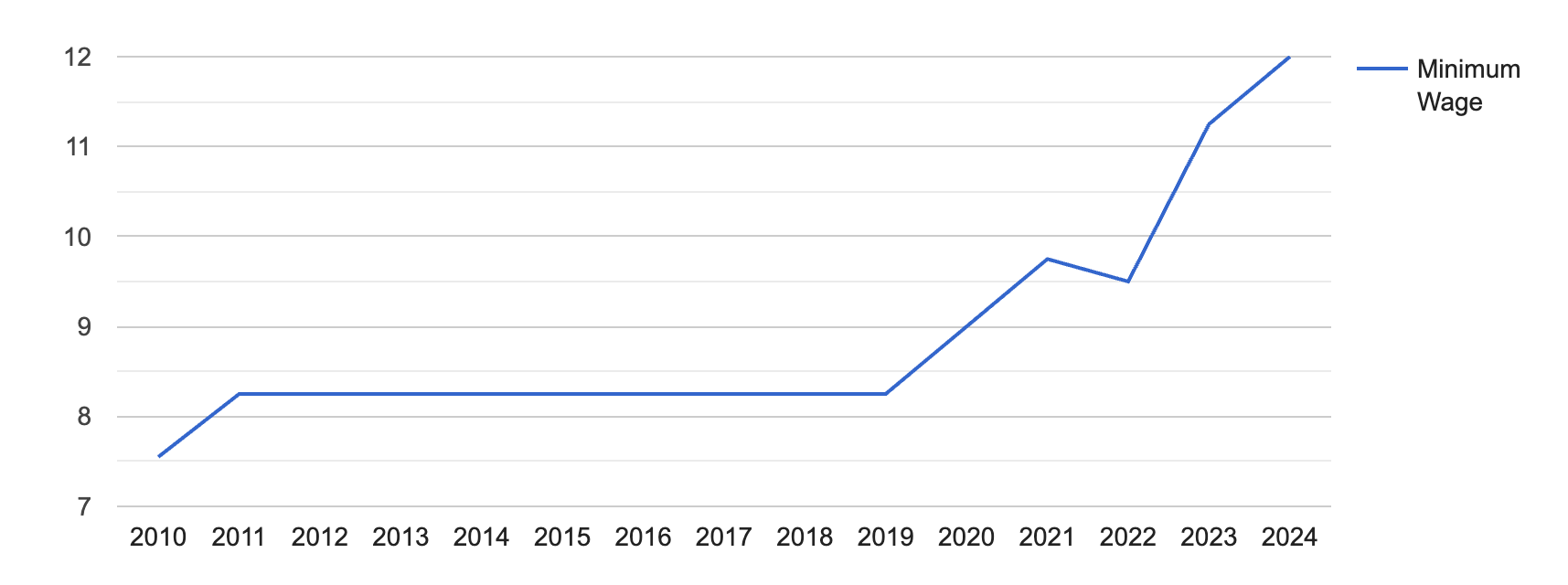
[Source: FRED]
You can also compare the Nevada minimum wage with the minimum wage in other states by interacting with the map below.
| State/District | Minimum wage |
| Alabama | $7.25 |
| Alaska | $11.73 |
| Arizona | $14.35 |
| Arkansas | $11 |
| California | $16 |
| Colorado | $14.42 |
| Connecticut | $15.69 |
| Delaware | $13.25 |
| Florida | $13 |
| Georgia | $7.25 |
| Hawaii | $14 |
| Idaho | $7.25 |
| Illinois | $14 |
| Indiana | $7.25 |
| Iowa | $7.25 |
| Kansas | $7.25 |
| Kentucky | $7.25 |
| Louisiana | $7.25 |
| Maine | $14.15 |
| Maryland | $15 |
| Massachusetts | $15 |
| Michigan | $10.33 |
| Minnesota | $10.85 |
| Mississippi | $7.25 |
| Missouri | $12.3 |
| Montana | $10.3 |
| Nebraska | $12 |
| Nevada | $12 |
| New Hampshire | $7.25 |
| New Jersey | $15.13 |
| New Mexico | $12 |
| New York | $15 |
| North Carolina | $7.25 |
| North Dakota | $7.25 |
| Ohio | $10.45 |
| Oklahoma | $7.25 |
| Oregon | $14.2 |
| Pennsylvania | $7.25 |
| Rhode Island | $14 |
| South Carolina | $7.25 |
| South Dakota | $11.2 |
| Tennessee | $7.25 |
| Texas | $7.25 |
| Utah | $7.25 |
| Vermont | $13.67 |
| Virginia | $12 |
| Washington | $16.28 |
| West Virginia | $8.75 |
| Wisconsin | $7.25 |
| Wyoming | $7.25 |
| District of Columbia | $16.5 |
[Source: FRED]
Tipped Employees
Employees earn the full minimum wage without any deductions for tips, as the state doesn’t allow employers to take tip credits.

Overtime Rules and Regulations in Nevada
Overtime rules and regulations in Nevada are designed to make sure that employees are fairly compensated for their time worked beyond the standard 40-hour workweek.
Employees must be paid 1.5 times their regular hourly rate for more than 40 hours in a single workweek.

Nonexempt Employees
Nonexempt employees — or those typically hourly and not exempt from overtime laws — are entitled to these overtime rates.
For example, if an employee earns $11.25 per hour, they should receive $16.88 per hour for any time worked over 40 hours in a week, resulting in a total weekly pay of $484.40.
Exempt Employees
In Nevada, exempt employees are — due to their job duties and pay — typically salaried workers who are not eligible for overtime pay under the Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA).
These employees often hold managerial, administrative or professional positions and meet specific criteria regarding their job duties and salary.
They must be paid a fixed salary that is not subject to reduction based on the quality or quantity of work performed.
Break Periods in Nevada
Break periods in the workplace are governed by both federal and state laws.
Nevada requires employers to provide a meal period of at least 30 minutes to employees who work a continuous period of eight hours.
This break is typically unpaid unless the employee is required to work through their meal period.
Family and Medical Leave Laws in Nevada
Nevada aligns with the federal Family and Medical Leave Act (FMLA), providing eligible employees with up to 12 weeks of unpaid, job-protected leave per year for certain family and medical reasons.
In Nevada, employers must follow FMLA rules if they have at least 50 or more employees for at least 20 weeks in the current or previous year.
Employees can take FMLA leave if they:
- Have been with the company for a year or more
- Have worked at least 1,250 hours over the past year
- Work at a place where there are 50 or more employees within a 75-mile radius

Reasons for FMLA leave include:
- Spending time with a newborn
- Recovering from a chronic health condition
- Looking after a family member with a serious health condition
- Managing urgent matters related to a family member's military service
- Caring for a family member who has been injured during military duty
Child Labor Laws in Nevada
Nevada employers should familiarize themselves with two primary laws: the federal FLSA and the Nevada Revised Statutes Chapter 609 (NRS 609), which focus on employing minors.
These laws cover three age groups of young workers: 16- or 17-year-olds, 14- or 15-year-olds and children under 14.
Work Permits
In Nevada, minors who are 14 and older don't need a work permit, or a Certificate of Employment, before they can legally work.
On the other hand, child labor laws in Nevada require minors under the age of 14 to obtain a work permit that’s signed by the court to be employed.
Working Hours and Maximum Number of Hours Children Can Work
Minors under 16 years of age are prohibited from working during night hours — for example, 4 p.m. until midnight. On the other hand, the state has no restrictions regarding night work for 16 and 17-year-olds.
Minors under 16 years of age can work up to eight hours a day and 48 hours a week. However, when school starts, they can only work three hours on a school day.
There are no set hour limits for 16- and 17-year-olds.
While child labor laws in Nevada sound straightforward, breaking them can lead to heavy penalties.
If employers don't follow Chapter 609, they can face fines of up to $2,500 for each time they break the rule, and they can even be charged with a misdemeanor.
Each penalty can lead to a separate fine, regardless of how many minors are involved.
Workplace Safety and Health Regulations in Nevada
In Nevada, workplace safety and health regulations are governed by both federal and state laws. The state operates under a federally approved Occupational Safety and Health Act (OSHA) which covers most private sector workers and all state and local government workers.
Nevada operates its own OSHA program or the Nevada Occupational Safety and Health Administration (Nevada OSHA). It conducts inspections, enforces standards and provides training and assistance to employers and workers.
Employers are required to provide a workplace without health and safety hazards. They must also provide training, safety equipment, and use of protective gear when necessary.
In addition, employees in Nevada have the right to report safety concerns, request Nevada OSHA inspections, and be free from retaliation for exercising their safety and health rights.
The last known data show there have been 43 fatal occupational injuries, most of which fall under transportation-related accidents.
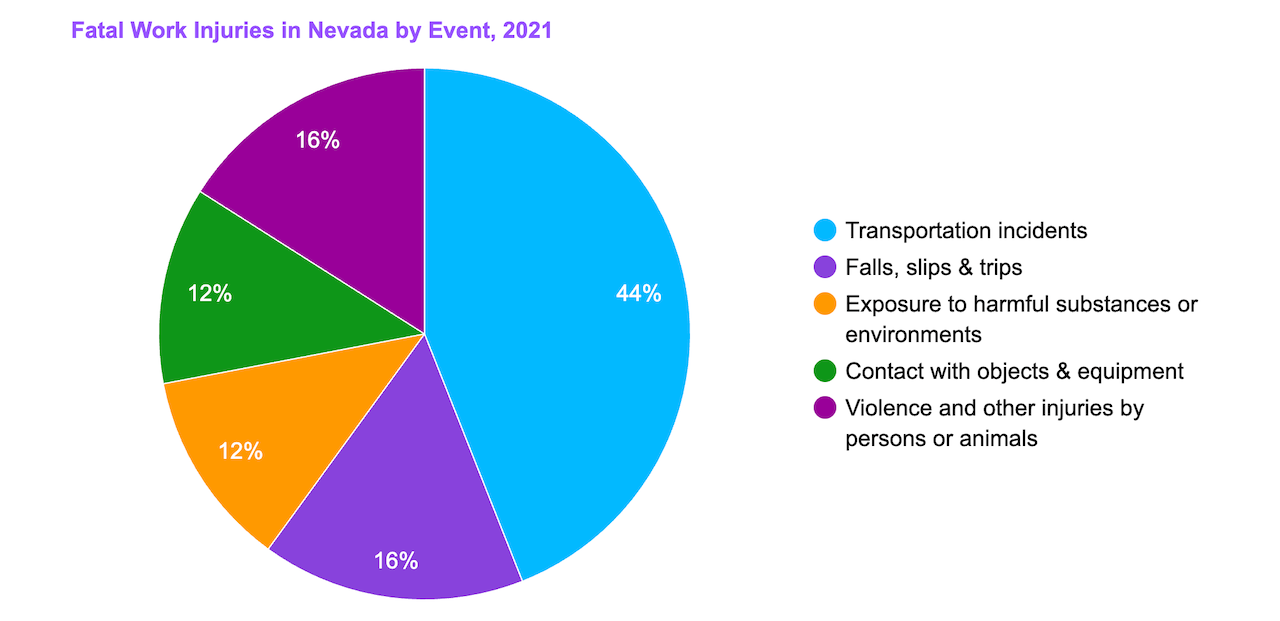
[Source: U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics]
You can see how Nevada compares to other states in the US when it comes to occupational fatal injuries by browsing the table below.
| State/District | No. of Fatal Work Injuries |
| Alabama | 111 |
| Alaska | 20 |
| Arizona | 67 |
| Arkansas | 74 |
| California | 462 |
| Colorado | 96 |
| Connecticut | 23 |
| Delaware | 13 |
| Florida | 315 |
| Georgia | 187 |
| Hawaii | 15 |
| Idaho | 30 |
| Illinois | 176 |
| Indiana | 157 |
| Iowa | 49 |
| Kansas | 63 |
| Kentucky | 97 |
| Louisiana | 141 |
| Maine | 19 |
| Maryland | 80 |
| Massachusetts | 97 |
| Michigan | 140 |
| Minnesota | 80 |
| Mississippi | 41 |
| Missouri | 147 |
| Montana | 40 |
| Nebraska | 39 |
| Nevada | 43 |
| New Hampshire | 21 |
| New Jersey | 110 |
| New Mexico | 53 |
| New York | 247 |
| North Carolina | 179 |
| North Dakota | 34 |
| Ohio | 171 |
| Oklahoma | 86 |
| Oregon | 66 |
| Pennsylvania | 162 |
| Rhode Island | 5 |
| South Carolina | 107 |
| South Dakota | 20 |
| Tennessee | 132 |
| Texas | 533 |
| Utah | 52 |
| Vermont | 10 |
| Virginia | 125 |
| Washington | 73 |
| West Virginia | 36 |
| Wisconsin | 105 |
| Wyoming | 27 |
| District of Columbia | 12 |
[Source: U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics]
Anti-Discrimination and Fair Employment Practices in Nevada
The Nevada Fair Employment Practices Act prohibits employers from discriminating against job applicants based on the following:
- Race
- Color
- Religion
- Sex
- Sexual orientation
- Age
- Disability
- National origin
- Genetic information
The Act applies to companies with 15 or more employees.
Termination in Nevada
Nevada is an "at-will" employment state, in which employers can terminate employees at any time for any reason, except for illegal reasons, such as discrimination.
The main exceptions to this rule are if an employee has a union contract or any employment agreement, whether it's written, verbal or implied.
It is illegal for an employer to retaliate against employees for exercising their rights.
Retaliation can take different forms, including termination, suspension, demotion, discipline or any form of discrimination when an employee stands up for their rights.
Final Paychecks in Nevada
Under Nevada Revised Statutes 680.020-NRS 608.040, employees who are terminated must receive their final wages within three days, while employees who resign should receive their final paycheck within seven days or on the next regular payday, whichever comes first.
To navigate Nevada's labor laws regarding termination, it's essential to have a clear understanding of your finances.
Use our Paycheck Calculator to estimate your take-home pay after taxes and deductions, according to Nevada's tax regulations.
Summary of Nevada Labor Laws
In Nevada, the minimum wage is set at $12.00 per hour for all employees.
When it comes to tips, the state mandates that employers must pay their workers the full minimum wage without taking any share of the tips.
Overtime pay must be 1.5 times the regular hourly rate for hours worked beyond a 40-hour workweek.
In addition, employees in Nevada are entitled to up to 12 weeks of unpaid, job-protected leave in alignment with the federal Family and Medical Leave Act (FMLA).
For every eight consecutive hours worked, employees must receive at least a 30-minute meal break.
Regarding employment of minors, those aged 14 and above are not required to have a work permit, while those under 14 must obtain a permit authorized by a judge.
For workplace safety, the state adheres to OSHA standards. The Nevada Fair Employment Practices Act protects job seekers from discrimination based on race, color, religion, sex, sexual orientation, age and other factors.
Following the at-will employment rule, both employers and employees in Nevada can terminate employment at any time for any lawful reason.
Terminated employees are entitled to receive their pay within three days, while those who resign should receive their pay within seven days or by the next regular payday, whichever comes first.
Frequently Asked Questions About Nevada Labor Laws
Find common questions surrounding Nevada labor laws below.
How many hours can you work in Nevada?
In Nevada, there are no limits on the number of hours an adult employee can work per day or week. However, employees under 16 years of age are restricted to a maximum of eight hours of work per day and no more than 48 hours per week.
Are employees paid overtime in Nevada?
In Nevada, employees must be paid overtime if they work more than 40 hours in a week or over eight hours in a day. A 'workday' is a 24-hour period that starts when the employee begins working.
How is overtime calculated in Nevada?
Overtime in Nevada is paid at a rate of 1.5 times the employee's regular rate of pay for hours worked more than 40 hours in a workweek, or for hours worked over 8 in a 24-hour period, unless otherwise exempt.
Are lunch breaks required in Nevada?
Yes, in Nevada, meal breaks are required under certain conditions. Employers must provide meal breaks of at least 30 minutes to employees who work a continuous period of eight hours.
This break is typically unpaid, unless the employee is required to work through their lunch break, in which case they will be compensated.
Disclaimer: This information serves as a concise summary and educational reference for Nevada state labor laws. It does not constitute legal advice. For personalized legal guidance, it is recommended to consult with an attorney.