North Dakota Labor Law Guide
A comprehensive guide to North Dakota labor laws: Covering key topics, including minimum wage regulations, overtime provisions, mandated breaks, hiring and termination procedures and other miscellaneous employment laws.
Key Takeaways of North Dakota Labor Laws
- North Dakota’s minimum wage is $7.25 per hour and has not changed since 2010.
- Employees in North Dakota are generally entitled to a 30-minute break in each shift exceeding five hours.
- Eligible employees are entitled to 1.5 times their regular rate of pay, or time and a half pay, for overtime at a minimum of $10.87 per hour for work exceeding 40 hours in 1 workweek.
- North Dakota is an at-will state, meaning both employers and employees can terminate their employment relationship without cause at any time.
- North Dakota is a right-to-work state.
Minimum Wage Regulations in North Dakota
North Dakota’s minimum wage is $7.25 per hour, with all of its municipalities following suit under a preemption law (House Bill 1193) that prohibits other municipalities from setting exclusive minimum wage rates.
| State/District | Minimum wage |
| Alabama | $7.25 |
| Alaska | $11.73 |
| Arizona | $14.35 |
| Arkansas | $11 |
| California | $16 |
| Colorado | $14.42 |
| Connecticut | $15.69 |
| Delaware | $13.25 |
| Florida | $13 |
| Georgia | $7.25 |
| Hawaii | $14 |
| Idaho | $7.25 |
| Illinois | $14 |
| Indiana | $7.25 |
| Iowa | $7.25 |
| Kansas | $7.25 |
| Kentucky | $7.25 |
| Louisiana | $7.25 |
| Maine | $14.15 |
| Maryland | $15 |
| Massachusetts | $15 |
| Michigan | $10.33 |
| Minnesota | $10.85 |
| Mississippi | $7.25 |
| Missouri | $12.3 |
| Montana | $10.3 |
| Nebraska | $12 |
| Nevada | $12 |
| New Hampshire | $7.25 |
| New Jersey | $15.13 |
| New Mexico | $12 |
| New York | $15 |
| North Carolina | $7.25 |
| North Dakota | $7.25 |
| Ohio | $10.45 |
| Oklahoma | $7.25 |
| Oregon | $14.2 |
| Pennsylvania | $7.25 |
| Rhode Island | $14 |
| South Carolina | $7.25 |
| South Dakota | $11.2 |
| Tennessee | $7.25 |
| Texas | $7.25 |
| Utah | $7.25 |
| Vermont | $13.67 |
| Virginia | $12 |
| Washington | $16.28 |
| West Virginia | $8.75 |
| Wisconsin | $7.25 |
| Wyoming | $7.25 |
| District of Columbia | $16.5 |
Regular Employees
Eligible regular employees are entitled to the current state minimum wage of $7.25 per hour in North Dakota, which matches the current federal minimum wage rate requirement.
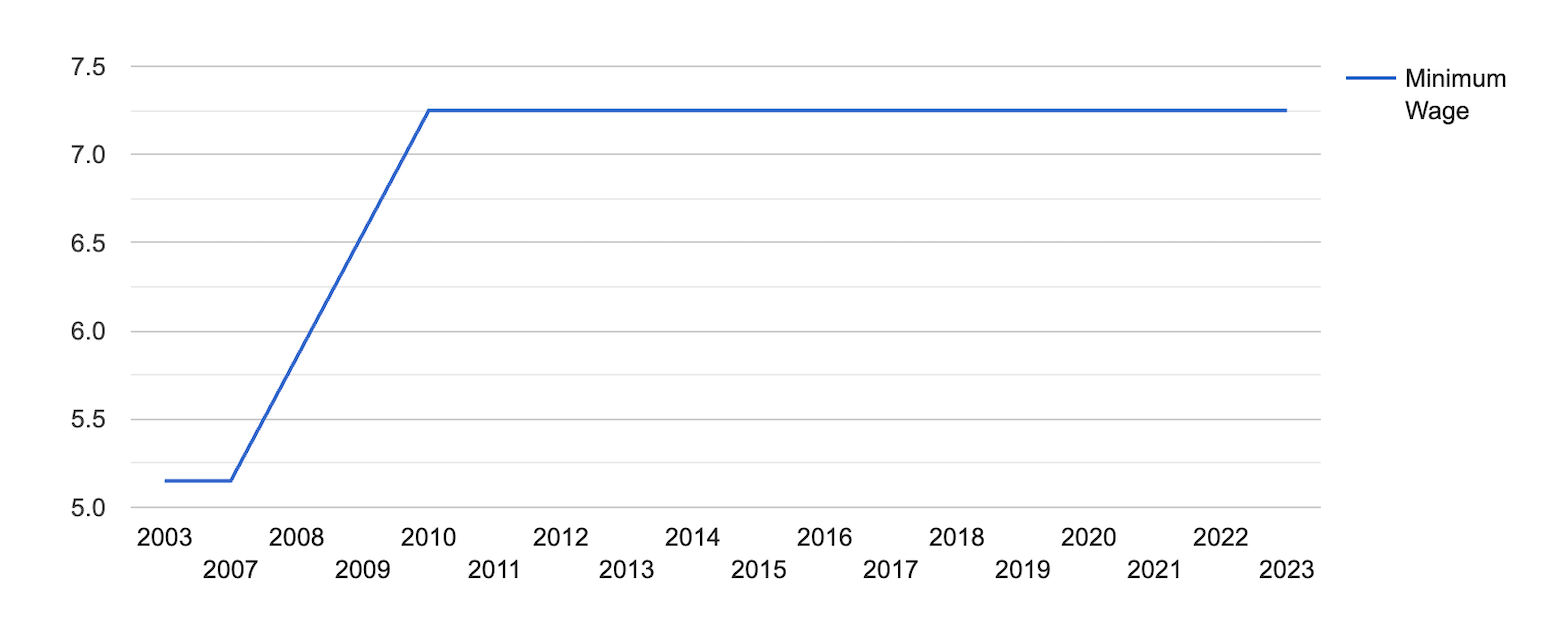
[Source: FRED]
North Dakota has kept its minimum wage the same since 2010 after increasing $6.55 in 2009.
Notably, despite this, hourly wages seem to be more dictated by market prices, with the average hourly earnings in North Dakota being $30.79 in 2022.
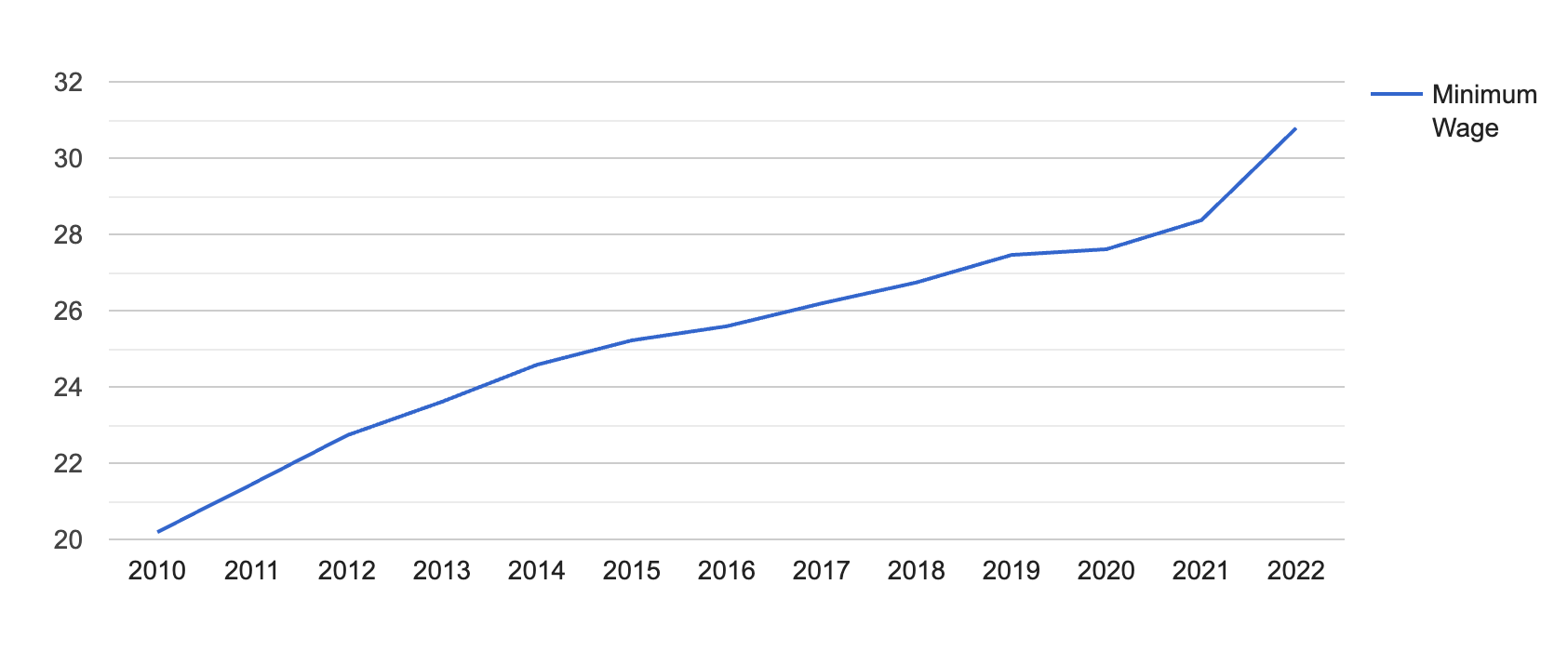
[Source: FRED]
Tipped Employees
Employees in North Dakota who receive more than $30 per month in tips can be paid a minimum direct wage of $4.86 per hour.
Tips earned in addition to the direct wage should be equal to the minimum wage of $7.25 per hour. If the total falls short, employers are responsible for making up the difference.
Employers should keep written records to verify that tipped employees are consistently paid at least the full minimum wage when their tips and direct wages are combined.
Keep in mind that in April 2023, as per House Bill 1158, North Dakota lowered the state’s personal income tax rates with three tax brackets: 0%, 1.95% and 2.5%. The highest prior to the law being passed was 2.9%.
For a convenient way to calculate your earnings after taxes and deductions, you can check out OysterLink’s Paycheck Calculator.
Overtime Rules and Regulations in North Dakota
North Dakota is aligned with federal overtime regulations outlined in the Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA), wherein the overtime rate is 1.5 times their regular rate of pay, or time and a half, for work exceeding 40 hours in 1 workweek.
Nonexempt Employees
Nonexempt employees in North Dakota are entitled to time and a half pay for overtime work at a minimum of $10.87 per hour.
Overtime must be calculated for each work week, regardless of the length of the pay period, including only the hours worked and excluding days off like vacation, paid holidays or sick leave.
Nonexempt employees cannot receive compensatory time off in place of monetary compensation for their overtime work.
Keep in mind that in North Dakota, taxicab drivers are entitled to overtime pay for any hours worked beyond 50 hours in a single work week.
Additionally, hospitals and residential care facilities have the option to establish a 14-day overtime period by agreement with their employees, provided that employees receive at least time and a half for hours worked exceeding 8 in a day or 80 hours within a 14-day work period.
To easily calculate your overtime earnings, check out our time and a half calculator.
Exempt Employees
Exempt employees are often salaried workers in administrative, executive, managerial or other professional positions and are not entitled to overtime pay.
For a complete description of exempt employees, check out this list by North Dakota’s Department of Labor and Human Rights.
At-Will Employment in North Dakota
North Dakota is governed by the employment-at-will doctrine, which means that either the employer or employee can sever their working relationship at any time with or without cause, except for discriminatory reasons, retaliation, public policy or other reasons prohibited by law.

Right-To-Work Laws in North Dakota
North Dakota is a right-to-work state, which upholds an individual’s right to secure employment without discrimination based on their union membership status.
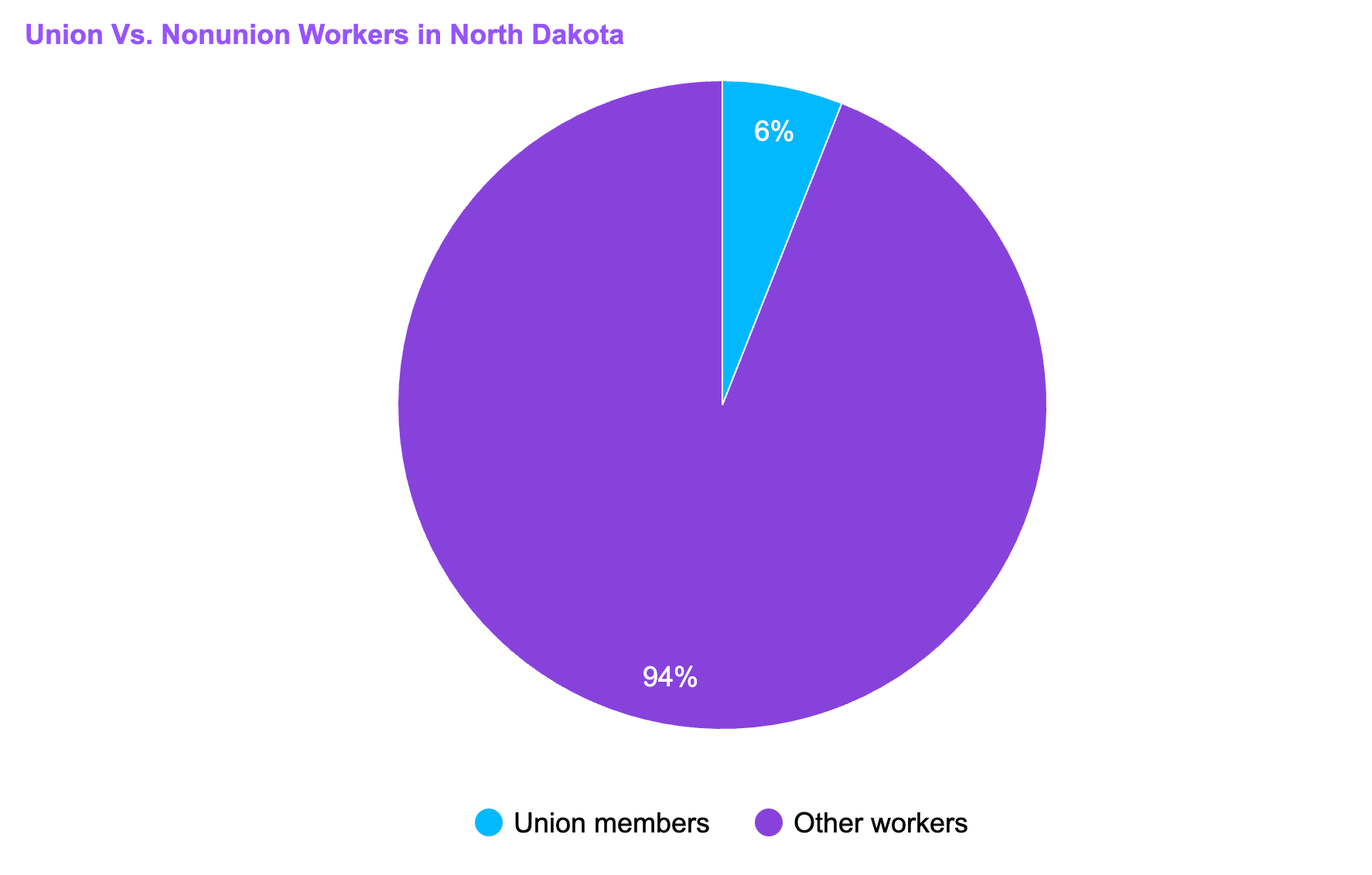
[Source: Victoria Advocate]
The union membership in North Dakota is lower than the country’s average at 10.1%.
Rest and Meal Breaks in North Dakota
State law requires 30-minute meal breaks for employees if their shift is longer than 5 hours.
There are no state or federal laws that require North Dakota employers to provide rest breaks.
Family and Medical Leave Laws in North Dakota
Employees in North Dakota are protected by the Family and Medical Leave Act (FMLA), which provides them with job-protected, unpaid leave for family and medical purposes.
Employees should provide a 30-day advance notice when leaves are expected. They may also be required to provide medical certification or proof of relationship for leaves involving care for their spouse, child or parent.
Family and Medical Leave Act
Under the FMLA, employees in North Dakota are entitled to take a leave for the following purposes.
You must meet the following requirements to qualify for the FMLA leave:
- Must have a minimum of 12 months (equivalent to 1 year) of employment with the company
- Should have worked at least 1,250 hours in the previous year
- Must be working at a location with a workforce of at least 50 employees within a 75-mile radius for a minimum of 20 weeks
Employers are obligated to follow FMLA requirements if their workforce consists of 50 or more employees and has been maintained for at least 20 weeks.
Uncompensated Family Leave Act for State Employees
North Dakota state employees are entitled to the rights under the Uncompensated Family Leave Act of 1989. As these are more generous than the FMLA, the provisions of this Act shall prevail.
To qualify for this leave, state employees should have worked for North Dakota for at least 1 year with 20 work hours or more per week.
Under this Act, state employees may extend their FMLA leave to 16 weeks.
Other Leave Laws
Here are the conditions for other possible types of leaves as per North Dakota labor laws:
- Jury duty: Employees on jury duty receive an approved paid leave of absence from work. However, the amount they earn from the court is subtracted from their regular pay. If they are on authorized annual leave during jury duty, their pay remains unaffected, and they can keep the court fee.
- Voting: Employers are not required to provide time off for employees in North Dakota to vote.
- Donor: Private employers are not required to provide time off for donor-related purposes. State employees, however, are entitled to paid leave of up to 20 days.
- Bereavement: Employers in North Dakota are not required to grant employees bereavement leave.
Workplace Safety and Health Regulations in North Dakota
North Dakota does not have its own state plan for safety and health in the workplace and instead follows federal law upheld by the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA).
Employers should observe OSHA standards in training, education, work safety and so on to avoid work injuries, illnesses and other safety concerns.
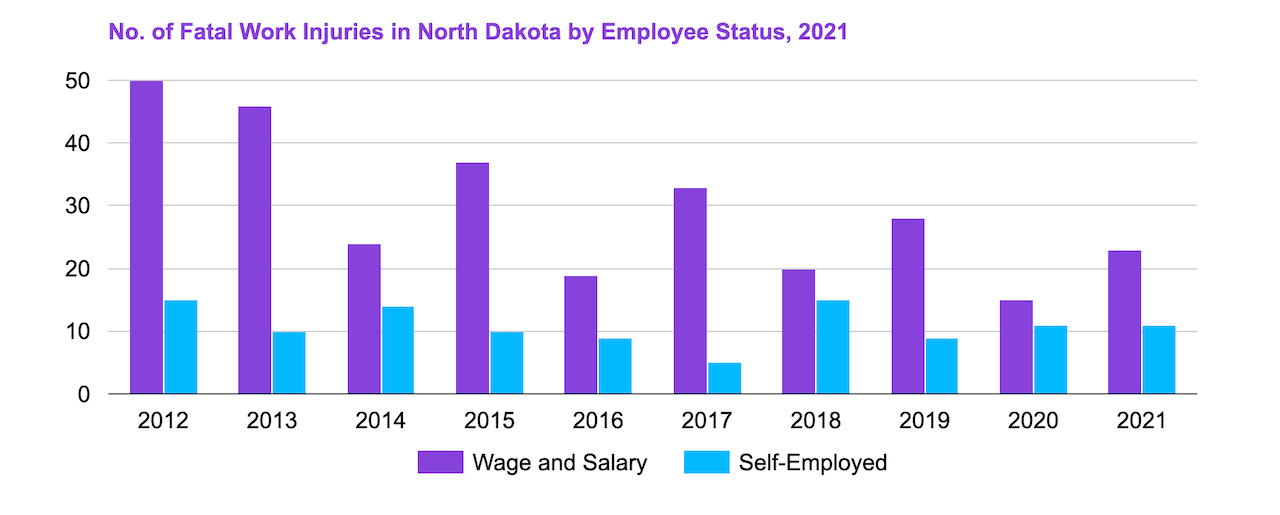
[Source: U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics]
There were 34 fatal occupational injuries in North Dakota in 2021—10 of which were due to transportation incidents and 8 due to contact with objects or equipment, accounting for 53% of all fatal work injuries.
| State/District | No. of Fatal Work Injuries |
| Alabama | 111 |
| Alaska | 20 |
| Arizona | 67 |
| Arkansas | 74 |
| California | 462 |
| Colorado | 96 |
| Connecticut | 23 |
| Delaware | 13 |
| Florida | 315 |
| Georgia | 187 |
| Hawaii | 15 |
| Idaho | 30 |
| Illinois | 176 |
| Indiana | 157 |
| Iowa | 49 |
| Kansas | 63 |
| Kentucky | 97 |
| Louisiana | 141 |
| Maine | 19 |
| Maryland | 80 |
| Massachusetts | 97 |
| Michigan | 140 |
| Minnesota | 80 |
| Mississippi | 41 |
| Missouri | 147 |
| Montana | 40 |
| Nebraska | 39 |
| Nevada | 43 |
| New Hampshire | 21 |
| New Jersey | 110 |
| New Mexico | 53 |
| New York | 247 |
| North Carolina | 179 |
| North Dakota | 34 |
| Ohio | 171 |
| Oklahoma | 86 |
| Oregon | 66 |
| Pennsylvania | 162 |
| Rhode Island | 5 |
| South Carolina | 107 |
| South Dakota | 20 |
| Tennessee | 132 |
| Texas | 533 |
| Utah | 52 |
| Vermont | 10 |
| Virginia | 125 |
| Washington | 73 |
| West Virginia | 36 |
| Wisconsin | 105 |
| Wyoming | 27 |
| District of Columbia | 12 |
[Source: U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics]
Therefore, the number of fatal injuries in North Dakota (34) is approximately 66.67% lower than the average number of fatal injuries in all states (102).
Child Labor Laws in North Dakota
The minimum age of employment in North Dakota is 14, with certain limitations for minors aged 14 and 15.
Teenagers aged 14 and 15 must adhere to specific regulations, including the need to file an Employment and Age Certificate for each job, restrictions on work hours and prohibitions on certain types of employment.
Minors aged 16 and above face no state restrictions but are subject to federal child labor laws.
Minors aged 14 and 15 can be exempt from certain rules when supervised by a parent or guardian, working in domestic service, engaged in agricultural employment or meeting specific school-related exemptions.
Babysitting is not considered employment unless it involves extensive hours over several weeks.
Working Hours
Minors aged 14 and 15 should adhere to the following work hours:
- Work hours: Between Labor Day and May 31, teens aged 14 and 15 are permitted to work between 7:00 a.m. and 7:00 p.m. From June 1 through Labor Day, work hours can be extended until 9:00 p.m.
- Daily work hour limits: On school days, work hours are limited to three hours; on nonschool days (weekends or holidays), up to 8 hours.
- Weekly work hour limits: In a school week, defined as any week from Sunday through Saturday when school attendance is required for at least four days, work is limited up to 18 hours. During a nonschool week, they can work up to 40 hours.
Antidiscrimination Laws in North Dakota
North Dakota citizens are protected by the North Dakota Human Rights Act, North Dakota Housing Discrimination Act and several federal laws.
These laws prevent discrimination or retaliation in employment based on age, color, marital status, mental or physical disability, national origin, participation in lawful activity, race, religion, sex and receipt of public assistance (state or federal).
Discrimination based on familial status and being a victim of domestic violence is considered a protected category only in housing matters and not in employment.
Independent Contractor Classification in North Dakota
To adhere to local tax and wage regulations, employers need to distinguish between employees and independent contractors. Employees work under the control of the employer, whereas independent contractors have greater independence in managing their trade or business.
North Dakota makes use of the “common law test” in determining whether an individual is an employee or independent contractor.
Official Holidays in North Dakota
Private employers in North Dakota are not obligated by law to offer their employees paid or unpaid holiday leave. For a list of the official state holidays in North Dakota, check the table below.
[Source: Secretary of State]
Termination and Final Paychecks in North Dakota
North Dakota law mandates that employees who were terminated or chose to resign should be issued a final paycheck on the next regular pay period.
Miscellaneous North Dakota Labor Laws
Learn more about other North Dakota laws in employment and labor relations.
Wage Payment
Employees must be paid all owed wages at least once a month. Other common pay frequency schemes include weekly, biweekly and semimonthly.
Unemployment Insurance
Unemployment insurance benefits offer financial support to those who lose their jobs through no fault of their own, helping bridge the income gap while they seek new employment, with no deductions from their wages.
Job Service North Dakota handles the administration of these benefits.
North Dakota Workers’ Compensation Law
North Dakota’s Workers’ Compensation law mandates that all employers, with only a few exceptions, must provide insurance coverage for all employees, whether they are full-time, part-time, seasonal or occasional workers.
It is illegal to deduct any part of the premium from an employee’s wages or salary.
Drug Testing
There are no legal restrictions on workplace drug testing, except when employers require employees to undergo drug or alcohol testing as a condition of getting or keeping a job, in which case they must cover the testing costs.
Smoking Laws
North Dakota was voted to become smoke-free in November 2012. This means that smoking, including e-cigarettes, is not allowed in all enclosed areas of public places and workplaces.
Gun Laws
Employers are prohibited from restricting employees’ possession of legally owned firearms in locked private vehicles parked on their premises or inquiring about such firearms.
They also cannot make employment conditional on concealed weapons licenses or the prohibition of legally owned firearms in locked vehicles for lawful purposes.
Firing or discriminating against employees for exercising their right to bear arms or self-defense is not allowed, provided firearms are not displayed on company property for reasons other than lawful self-defense.
Employers are not legally responsible for enforcing these restrictions and are shielded from liability in criminal or civil cases for adhering to this law.
Frequently Asked Questions About North Dakota Labor Laws
Read on for answers to frequently asked questions regarding North Dakota labor laws.
What is the legal working age in North Dakota?
The legal working age in North Dakota is 14 years old, with several limitations for those aged 14 and 15 in terms of work hours and occupations.

What is the minimum wage in North Dakota?
North Dakota’s minimum wage is aligned with the federal wage rate of $7.25 per hour.
What are the termination laws in North Dakota?
Given how North Dakota is an employment-at-will state, both employers and employees can terminate their working relationship for any reason at any time—except for reasons specifically prohibited by the law.
Am I entitled to a rest break in North Dakota?
The short answer is no. North Dakota law only mandates meal breaks of at least 30 minutes for each shift exceeding 5 hours. However, some employers have more generous policies, which should be discussed during the hiring process.
How much is the income tax rate in North Dakota?
North Dakota’s individual income tax is structured as a graduated tax, with rates varying from 1.10 percent to 2.90%. In addition, the state levies a corporate income tax, which falls within the range of 1.41% to 4.31%.
How is overtime paid in North Dakota?
Overtime, or hours exceeding 40 hours in 1 workweek, should be paid at time and a half or 1.5 times the employee’s regular rate of pay.
What is a livable salary in North Dakota?
According to an MIT study, a livable salary for a single person in North Dakota is at least $15.35 per hour.
Disclaimer: This information serves as a concise summary and educational reference for North Dakota labor laws. It does not constitute legal advice. For personalized legal guidance, please consult an attorney.