Fast-Food Worker Salary in the United States
The average base salary for a Fast-Food Worker in the United States is $2,509 a month, or $30,110 per year, according to the latest Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) data.
Fast-food workers rarely receive tips; unlike in sit-down restaurants where 92% of individuals always or often leave a tip, only 12% do so at fast-food establishments with no Servers.
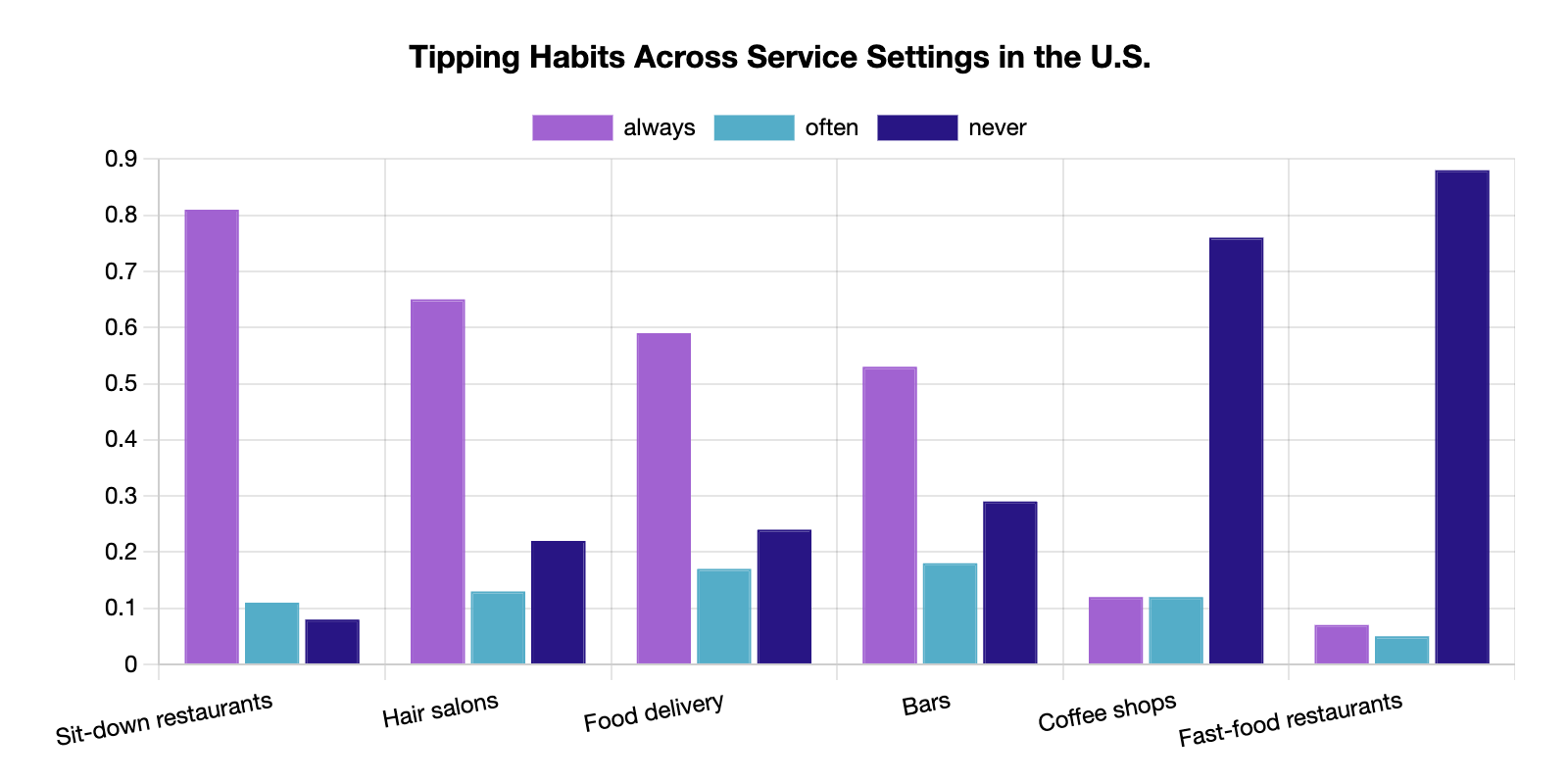
[Source: Pew Research]
How Much Does a Fast-Food Worker Make Hourly?
The average hourly wage for a Fast-Food Worker is $14.47. This is well below the national average which stands at roughly $28 per hour but above the federal minimum wage of $7.25 an hour.
If you'd like to know how your current or target Fast-Food Worker salary compares across the country, try out our tool below.
Fast-Food Worker Salary by Year
Currently, the salary of a Fast-Food Worker is at an all-time high and is approximately 33.7% higher than what it was five years ago.
Check out the chart below for detailed insights into Fast-Food salaries over the last five years.
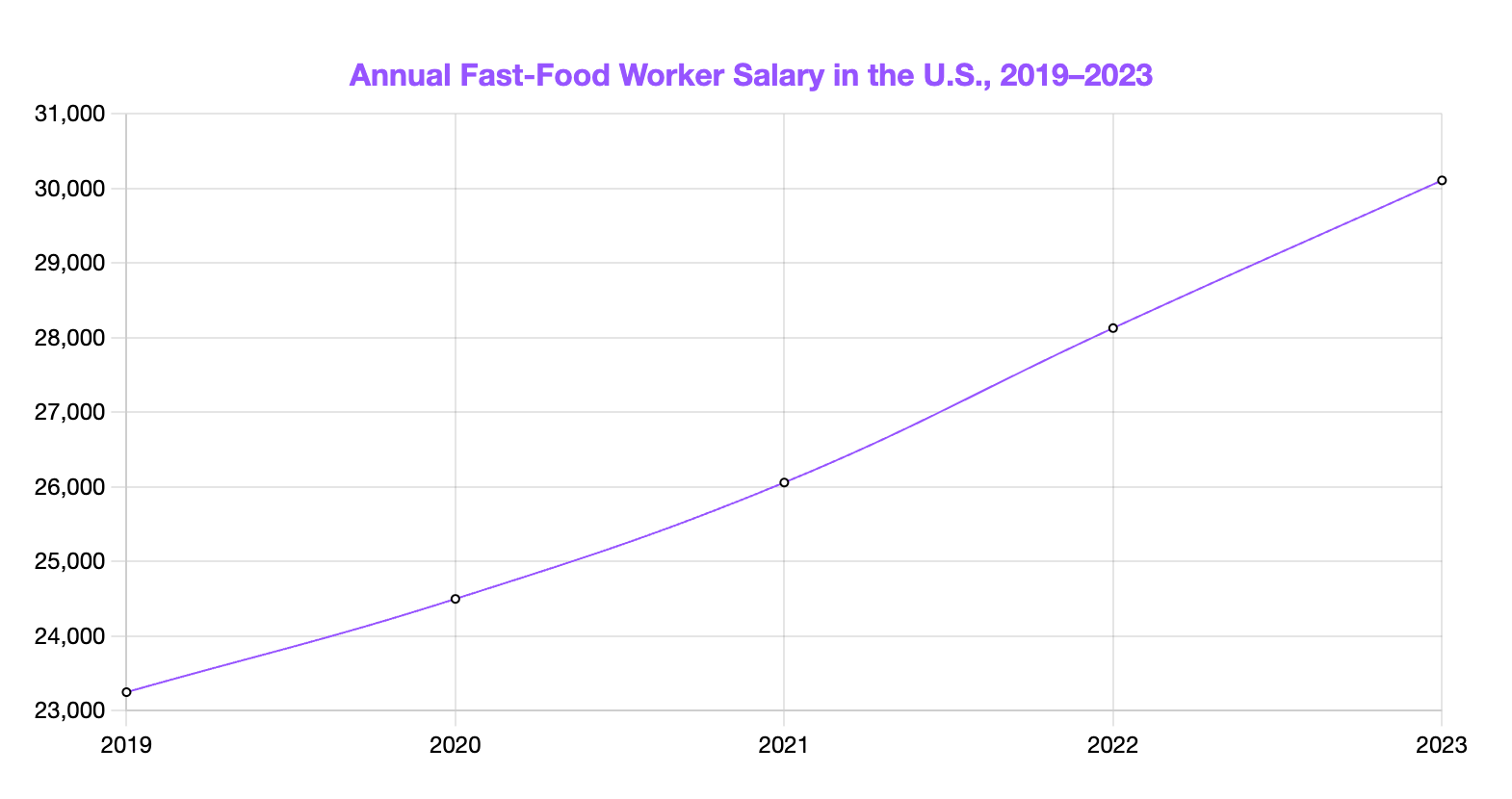
[Source: Bureau of Labor Statistics]
How Much Does a Fast-Food Worker Make Weekly?
The weekly salary for a Fast-Food Worker stands at $579.2, which is about 40.38% of what a typical worker in the U.S. earns.
What Is a Typical Salary Range for a Fast-Food Worker in the U.S.?
Some Fast-Food Workers may earn as little as $22,190 annually. This places them at the 10th percentile.
Others might earn as much as $36,880 per year, which positions them at the 90th percentile of all Fast-Food Workers earners.
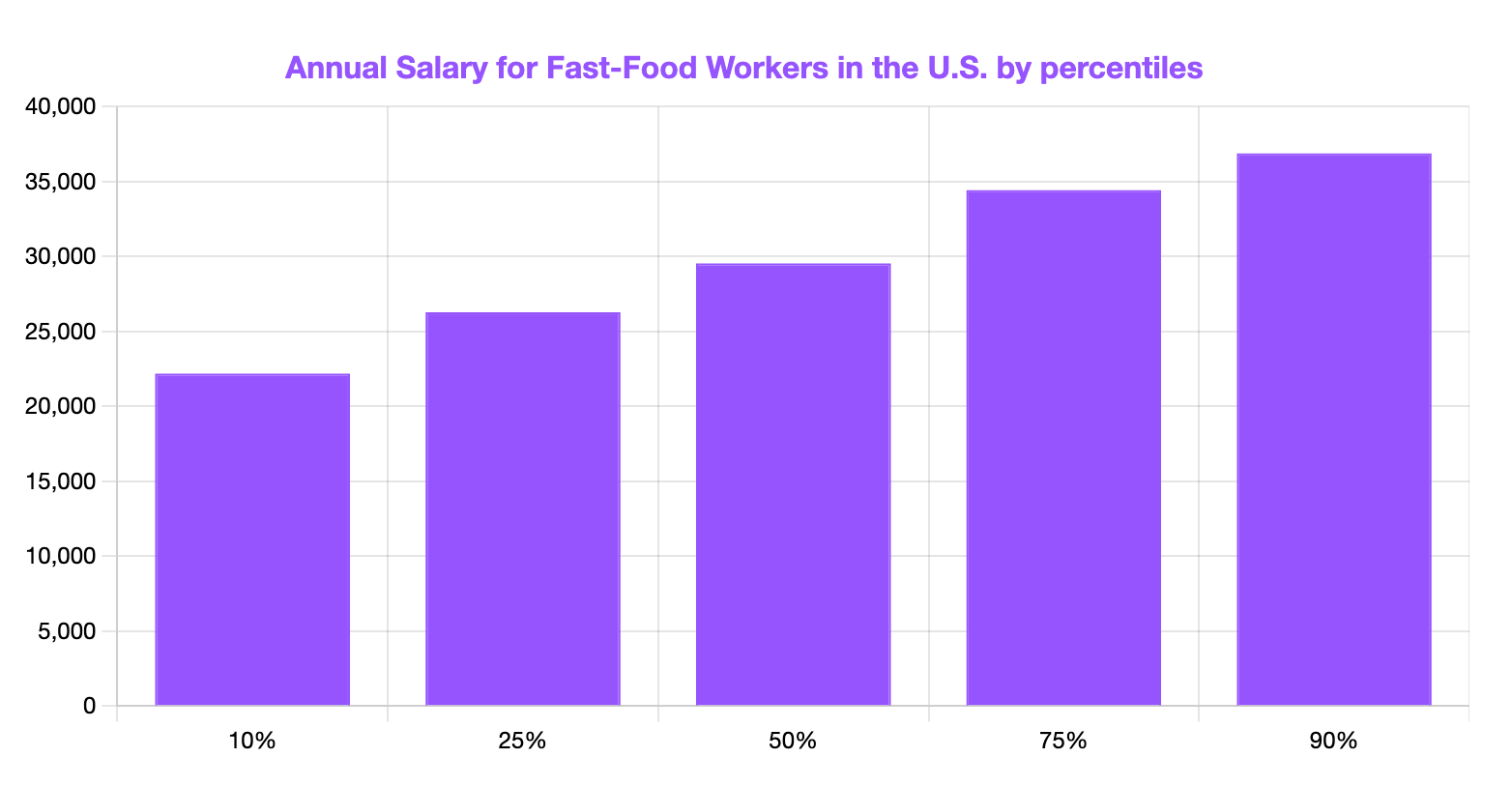
[Source: Bureau of Labor Statistics]
Simply put, if you are in the 90th percentile, you earn more than 90% of all the Fast-Food Workers in the United States.
Consequently, a salary of $36,880 would put you among the top 10% of earners in this profession.
Earning $22,190 would place you within the bottom 10% of earners among Fast-Food Workers.
What Impacts Your Fast-Food Worker Salary?
Several factors can influence your earnings as a Fast-Food Worker, including:
- Location: How much you earn as a Fast-Food Worker can vary significantly depending on the region you are performing your job. This is mostly because different states or cities have different costs of living, minimum wage laws and local economic conditions.
- Experience: The more experience you gain as a Fast-Food Worker, the higher the salary you’ll receive. This is especially true if you have specialized skills such as inventory management or team leadership, that make you more valuable to your employers.
- Establishment: Different fast-food chains offer different wage structures and benefits, which can impact your average salary. For instance, McDonald’s has a better compensation culture than Burger King, according to the Comparably data.
- Position: Like in most industries, salaries in the fast-food industry can vary based on the specific position. For example, if you are performing a role of a manager or a supervisor you will typically earn a higher salary than those at entry-level positions.
- Shifts and hours: Even though premium pay for weekends and night shifts is not regulated in the Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA), some employers can reward this type of work with higher hourly rates.
- Economic factors: General economic conditions in your region, such as inflation rates and unemployment levels can dictate wage trends in the fast-food industry and other industries for that matter.

Explore the chart below to discover industries with the highest levels of employment for Fast-Food Workers in the U.S.
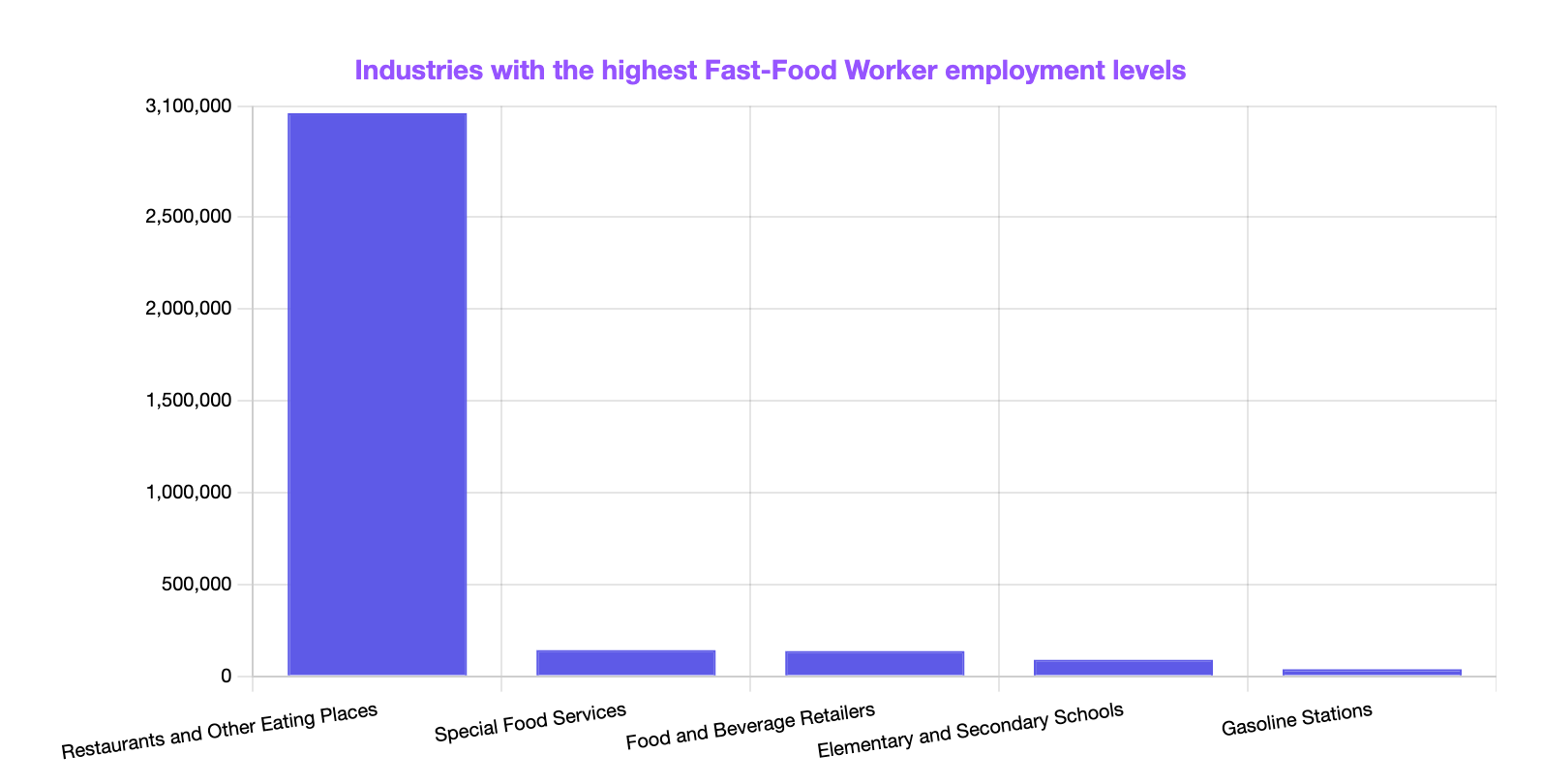
[Source: Bureau of Labor Statistics]
Estimate Your Take-Home Pay
Are you a Fast-Food Worker in the United States? Check out our paycheck calculator to estimate your take-home pay.
Explore our state-specific calculators, customized for each state to include local tax laws and deductions.
When using our paycheck calculator, follow these four simple steps:
- Step 1: Enter your gross earnings (the total amount before tax deductions)
- Step 2: Choose your pay frequency (hourly, daily, weekly, biweekly, monthly or annually)
- Step 3: Select the state where you are employed
- Step 4: Hit the Calculate Tax button and get the results
Highest-Paying States and Districts for Fast-Food Workers
Three of the highest-paying areas for Fast-Food Workers in the U.S. are the District of Columbia, Washington and California.
You can also see the table below, organized from the highest- to lowest-paying.
If you want a better overview of how average Fast-Food Worker salaries vary across the U.S., check out the map below.
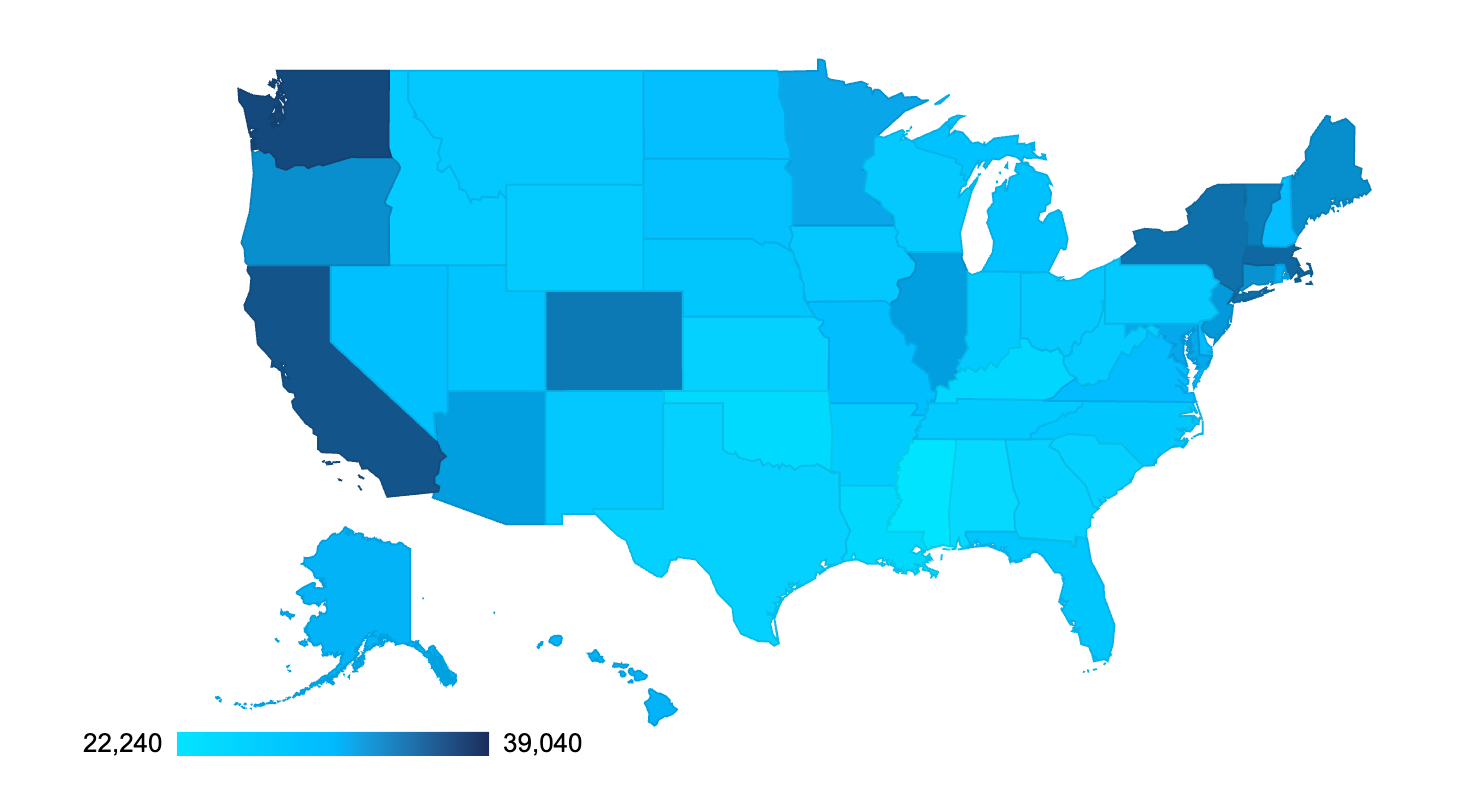
[Source: Bureau of Labor Statistics]
Fast-Food Worker Salary in Four Major US Cities
The four major cities in the U.S., New York City, Los Angeles, Miami and Chicago, offer different Fast-Food Worker salaries.
Among them, Los Angeles has the highest wages for Fast-Food Workers, followed by New York, Chicago and Miami.

[Source: Bureau of Labor Statistics]
How to Negotiate Your Fast-Food Worker Salary
To maximize your pay working in a quick-service restaurant, try the following techniques:
- Emphasize your worth: When negotiating salary it’s best to focus on your skills and experience to show your employer what you bring to the table. Mention your previous roles and give an example of how you impacted the overall efficiency of your prior team.
- Research salary trends in your area: Your salary expectations should be realistic. This is why it is important to know what is the usual wage range for the position you are applying to.
- Come up with a specific number: Once you’ve researched the salary trends, aim for the higher range but be ready to compromise. For instance, you can accept lower pay but condition them to give you a raise after three or six months.
Non-Monetary Benefits for Fast-Food Workers
As a Fast-Food Worker, you can expect some of the following benefits that stretch behind your salary:
Employee discounts
Working in a fast-food establishment often comes with employee discounts such as reduced prices on food and beverages which sometimes apply to your immediate family members as well.
Flexible schedules
Flexible scheduling is a common practice in the fast-food industry where you, as an employee, have the freedom to customize your work hours. This can be very beneficial if you are trying to juggle your job with other responsibilities such as school or family obligations.
Paid time off
Paid time off (PTO) is one of the most important non-monetary benefits you can have as an employee in the fast-food industry as you can time some off without sacrificing your income. PTO includes paid vacation days, sick leave, parental leave, jury duty, bereavement leave and disability leave.
According to Forbes, only 43% of hospitality workers have access to paid time off.
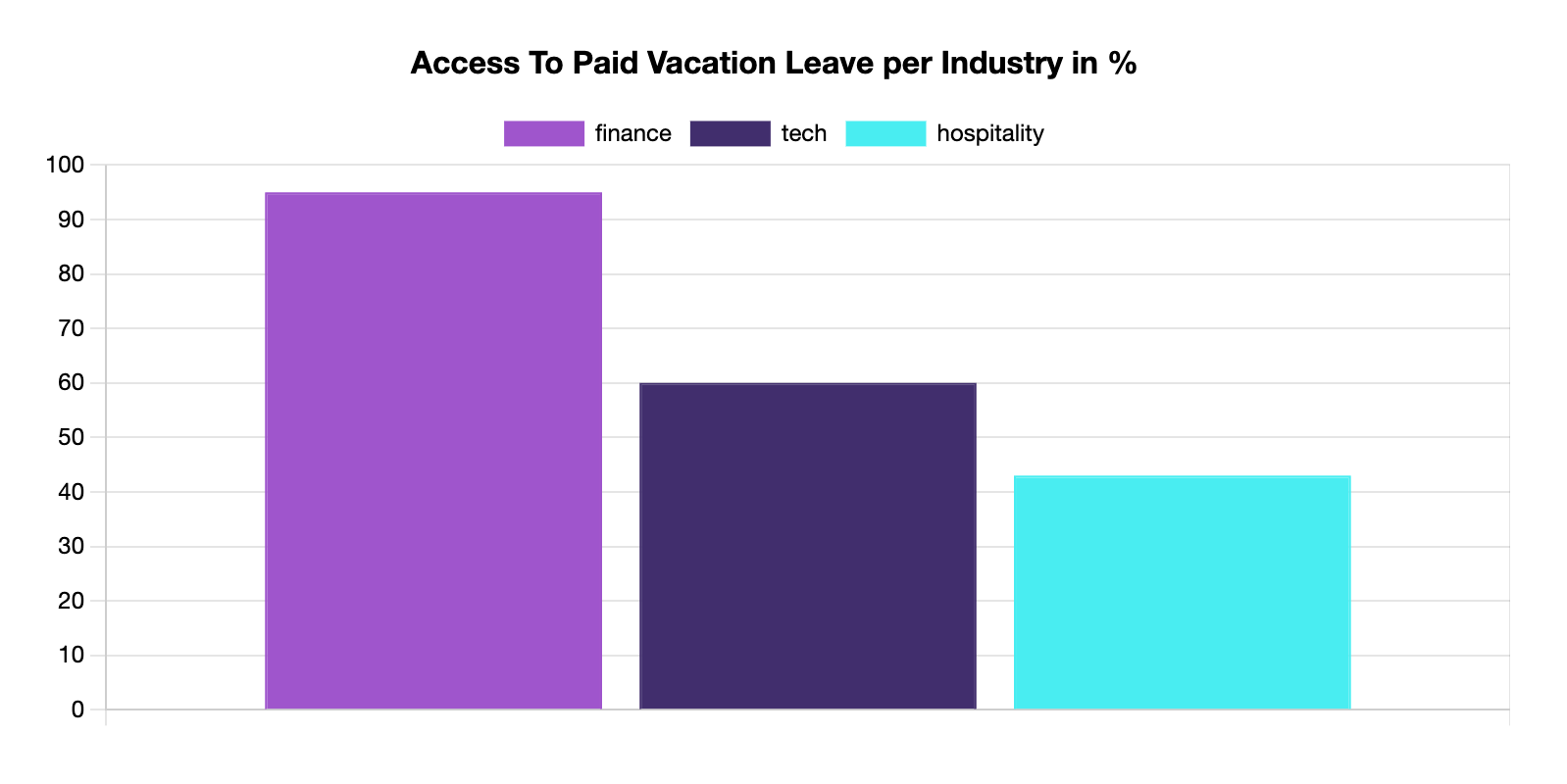
[Source: Forbes]
Healthcare benefits
Healthcare benefits typically refer to health insurance plans that cover medical, dental and vision expenses. This helps you maintain your health and creates a sense of security should something unpredictable happen.
Recognition programs
Recognition programs are employers’ initiatives that aim to acknowledge and reward employees for their outstanding performance, contributions or achievements.
This may include:
- Employee of the month
- Performance-based awards
- Service milestones
- Team celebrations
How Much Do Job Positions Similar to a Fast-Food Worker Get Paid?
Fast-Food Workers are among the lowest-paid positions in the restaurant industry. Still, they earn more than Bussers and Food Runners but less than Waiters/Waitresses.
How We Collect Our Salary Data
We at OysterLink, get our salary data from the latest information available on the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) official website. We also take into account estimates from the number of job search sites. Discover our methodology in more detail.
 | Expert Reviewer Milos Eric thoroughly evaluated this salary guide to ensure the accuracy and comprehensiveness of the analyses provided. The salary guide provides insights such as location-specific figures, industry trends and factors that influence compensation. As the Co-Founder and General Manager of OysterLink, Milos brings his extensive experience as an entrepreneur and business executive. Through the years, he has led and hired more than 500 employees for global companies like DesignRush and Digital Silk. Not to mention, he is recognized as a Top Voice for Leadership, Recruitment and Recruitment Management on LinkedIn. |
