Guide to a Cashier Career
This article will cover all the necessary information related to the role, including what Cashiers do, their duties and responsibilities and what their typical workday looks like.
For those who are looking to become a Cashier, we have a section where we explain how to get a job as a Cashier without prior experience.
We also list the top skills that employers are looking for when hiring for the role. For more information on how to prepare for the interview, you can check out some of the most common Cashier interview questions on our site.
What Is a Cashier?
In the hospitality industry, Cashiers operate the cash register and are in charge of processing cash and card transactions at the counter. They are also responsible for handling refunds and returns by following company-specific policies.
Depending on the job post, Cashier responsibilities might also include inventory management, which involves monitoring stock inventory and placing orders when products are in low supply.
Since they interact with customers on a daily basis, Cashiers are also expected to provide stellar customer service by being polite and friendly.
What Does a Cashier Do?
Some of the typical day-to-day Cashier responsibilities include:
- Operating the cash register, processing payments and issuing receipts to customers
- Maintaining and troubleshooting POS systems
- Greeting customers as they enter the store
- Providing excellent customer service by addressing questions and customer complaints
- Prioritizing customer-related tasks during busy periods at work
- Handling refunds and returns in accordance with the company’s policies
- Closing the cash register at the end of the shift
Cash register closure
As a Cashier, you will occasionally have to perform end-of-day cash box closing and confirm all of the financial records line up. You might be asked to do this at the end of the shift when your focus and energy levels are lower, so make sure this is something you can deal with before applying for a job as a Cashier.
In order to maintain clear financial records, you should follow a simple and effective approach that will ensure your reports are always accurate. Whilst different employers deploy different strategies to close the cash register, make sure to familiarize yourself with the best practices using this video below.
Top Skills and Qualities of Successful Cashiers
The most important Cashier skills are those you need to perform these three key tasks:
- Operate the cash register in a timely and organized manner
- Be polite and address customer concerns and questions with empathy and understanding
- Proactively assist customers when they need help
Therefore, the best Cashiers excel at math and accounting. They’re able to calculate costs quickly and efficiently, while simultaneously attending to their customers’ needs.
Cashiers might also be asked to provide a report at the end of each workday. To deliver optimal results, Cashiers should inspect the report and look for discrepancies in the balance sheet.
It’s also not uncommon to run into inconsistencies while balancing the cashier drawer at the end of the day. However, it’s important to proactively address and solve problems before they can cause any financial or budget issues.
To ensure customer satisfaction while processing their payments, Cashiers must also interact with them in a friendly demeanor. For this, they need strong customer service skills and general interpersonal skills.
These skills also help when addressing customer complaints. It’s the Cashier’s responsibility to ensure they feel valued and understood while helping them resolve the issue.
Career objective for Cashier
Most of the time, Cashiers handle money transactions and deal with customers at the counter. While this might seem repetitive and boring, the skills and experience a Cashier gains working behind the counter can be incredibly valuable for their career.
With previous sales experience and a proven track record of providing awesome customer service, Cashiers can easily transition to similar roles that require the same set of skills — such as Host/Hostess, Waiter/Waitress and Receptionist.
How To Become a Cashier?
In this section, you can learn the basic requirements for landing a Cashier job and how to get hired without previous experience in the role.
What are the requirements to be a Cashier?
A high school diploma might be necessary to land a Cashier job. However, given that you can work as a Cashier at 14 in the U.S., this may not always be a requirement.
Establishments typically provide on-the-job training and teach new employees everything from how to interact with customers to how to operate a POS system.
How to become a Cashier with no experience
Since the Cashier role is an entry-level one, the only thing establishments may require from candidates is a high-school diploma.
However, establishments may sometimes look for individuals with previous experience in the role. If this is the case, the establishment will mention it specifically in its Cashier job description.
Therefore, when applying for jobs, it’s important to go through every job posting thoroughly and check how your resume aligns with what the establishment is looking for.
To increase your chances of getting hired, you can learn how to use POS systems. Although numerous systems are in use, learning how to operate one is usually enough. Switching between different interfaces shouldn’t pose an issue for an experienced Cashier. You can also watch informative POS system videos on YouTube, such as this one:
If you're curious to know what POS systems are currently most widely used in the U.S., refer to the graph below.
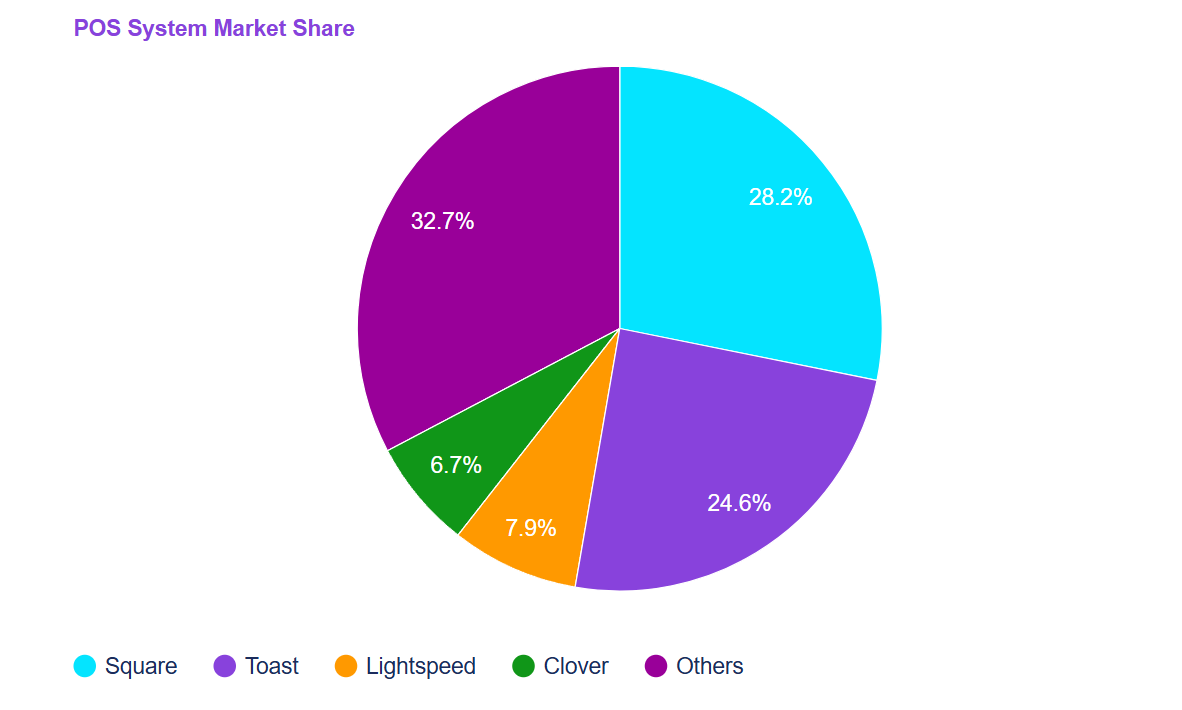
[Source: 6sense]
Ideally, the next step would involve getting a part-time Cashier job and learning on the go. That way, you would be able to improve your skills with the help of a senior colleague. If that’s not an option, look for similar roles where you can gain valuable skills and experience until you transition to the Cashier role.
While at work, focus on interacting with customers. For starters, you can try greeting them politely and asking if they need any help as they approach the counter. To hone your communication skills, observe your colleagues and simply replicate what they do. Over time, you will naturally become more confident in interacting with customers.
Cashier Industry Trends in 2024
The most recent data from BLS shows that there were around 3,298,660 Cashiers employed in the U.S. in 2023. However, due to the increase in the use of technology and self-service checkouts, it's expected that there will be a 10% decline in the number of Cashiers in the next 10 years.
The good news is that, over the next decade, there will be an average of 577,600 Cashier jobs posted each year in the United States. The reason behind this is the workers who are exiting the labor force to retire as well as people being promoted to other, more senior roles.
What Is the Work Environment of a Cashier Like?
Cashiers work in all types of establishments with cash registers, including supermarkets, food stores, hardware stores and other retail settings. In the hospitality industry, they can be found in restaurants, hotels, cafes and bars.
Wherever they work, they’re surrounded by customers who might look for their help. Aside from processing their payments, Cashiers also often assist customers in locating items and resolving issues that arise during their time at the establishment.
It’s also up to Cashiers to resolve customer complaints and handle returns and refunds. When doing so, they might have to interact with unsatisfied customers and ensure the situation is handled with patience and empathy while following policies set by their company.
Cashiers spend a lot of time on their feet and may occasionally be required to lift heavy objects. Therefore, it’s also important to possess enough physical stamina for the Cashier job.
The role can be part-time or full-time, and the work schedule may vary depending on the establishment’s shifts and hours.
Pros and Cons of Being a Cashier
A Cashier job can be rewarding but it also comes with certain challenges. With that said, let’s explore the pros and cons associated with this role.
Pros:
- Job demand: Due to large levels of customer demand for retail services, finding a Cashier job usually isn’t difficult.
- Social interaction: The Cashier job offers plenty of opportunities for social interaction, which is a positive for people who enjoy working with others.
- Employee discounts: The types of stores Cashiers work in usually offer 10-20% discounts for employees.
- Skill development: Working as a Cashier is a good way to develop multitasking and customer service skills, both of which can be beneficial for career progress.
- Rapid advancement: Good Cashiers can quickly become eligible for management positions such as Shift Supervisors and Store Assistants, which can impact their salary in a positive manner.
Cons:
- Low job security: Although it may not be difficult to land a Cashier job, employees in the role are highly replaceable due to the low education and experience requirements.
- Low salary: Cashiers in the U.S. make $14.77 per hour, which is less than some other entry-level positions such as Waiter/Waitress and Prep Cooks.
- Dealing with unsatisfied customers: The role often sees Cashiers deal with unsatisfied customers when addressing customer complaints and handling returns/refunds.
- Time pressure: One of the most challenging aspects of the Cashier job is managing time pressure at the checkout counter.
Irregular hours: Cashiers often have unpredictable schedules and may have to be available on evenings, weekends and holidays.
