Restaurant Industry Inflation: Key Findings
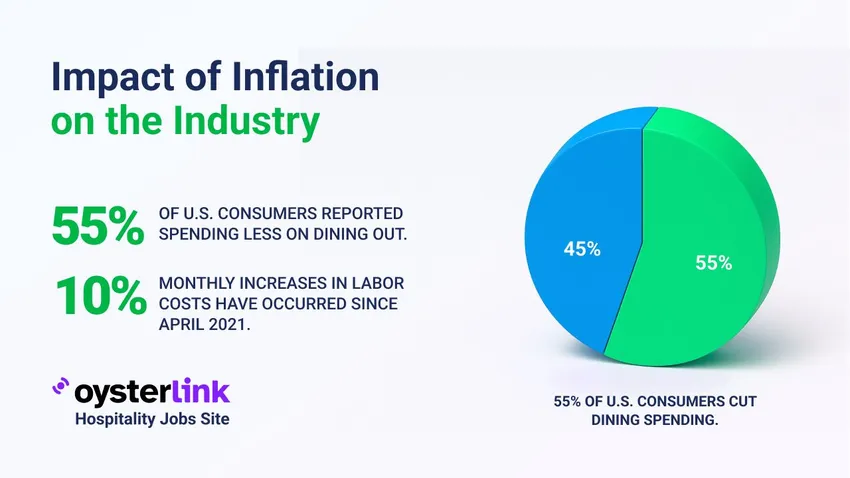
- Labor costs have been rising by 10% per month since April 2021.
- In 2023, 82% of operators increased menu prices; 61% plan more increases in 2024.
- As of November 2024, 53% of restaurant operators were still paying off pandemic-related debt.
- In Q3 2024, 55% of consumers reported spending less on dining out.
Restaurant industry inflation has affected every facet of operations in recent years, from food and labor costs to consumer behavior and pricing strategy.
While inflation has cooled from its peak, it continues to influence how restaurants operate, price their offerings and interact with customers.
This report compiles the most recent data to show how restaurant industry inflation reshaped the sector between 2020 and 2025.
Impact of Restaurant Industry Inflation on Employment and Labor Costs
Labor has been one of the hardest-hit operational costs during the inflation period.
Since April 2021, labor expenses have increased by approximately 10% per month.
This is driven by a combination of rising minimum wages, growing worker expectations and a competitive labor market.
Small and mid-sized restaurants, in particular, have struggled to keep up. Many have adopted digital tools — like AI-powered scheduling, QR code menus and kiosk ordering — to reduce reliance on labor.
Operators are also adjusting business hours and reducing shifts to better match demand patterns.
How Restaurant Industry Inflation Is Driving Up Operating Costs and Supply Expenses
From rent and utilities to packaging and processing fees, non-food-related costs have also surged.
Rent for some operators has increased by 15% since 2019. Utility expenses, particularly electricity and gas, have seen significant upticks, with electricity costs up 10.2% and transportation services up 13.9% year-over-year.
Paper goods and other disposable supplies have quadrupled in price since the pandemic began, adding to the strain on margins.
Many restaurants have turned to bulk purchasing, renegotiated contracts or transitioned to digital and reusable options where possible.
Restaurant Industry Inflation’s Impact on Menu Prices in Full-Service and QSRs
To keep up with rising costs, restaurants have been forced to raise prices.
In 2023, 82% of operators increased menu prices, and 61% plan to do so again in 2024. Menu prices for full-service restaurants have climbed 8.8% since 2022.
Quick-service restaurants (QSRs) have also seen steep increases:
- Chipotle: +14%
- McDonald’s: +8%
- Applebee’s: +7%
- Chili’s: +9%
- IHOP: +11%
Despite these increases, price hikes are rarely enough to fully cover the rise in operating costs, leading operators to make incremental adjustments and implement value-added promotions.
See also: How To Budget a Restaurant: A Guide for New Restaurant Owners and Managers
Restaurant Industry Inflation, Closures and Debt
Approximately 90,000 restaurants have closed since early 2020, either temporarily or permanently.
These closures reflect both the immediate impact of the pandemic and the long-term challenges of operating with thin margins and rising costs.
As of November 2024, 53% of restaurant operators were still servicing debt incurred during the pandemic.
The financial burden remains high for many, with limited room for error. While many restaurants have survived, they continue to face economic fragility due to rent increases, high-interest loans and inflationary cost structures.
Restaurant Industry Inflation, Consumer Behavior and Dining Frequency
Consumers have become more price-sensitive, leading to behavioral shifts that impact restaurant traffic.
In Q3 2024, 55% of consumers reported spending less on dining out, and 57% said they now eat at home more frequently than they did pre-pandemic.
According to PYMNTS — a research platform focused on payments and commerce data — 78% of surveyed consumers plan to eat at home more in the future as a cost-saving strategy.
When choosing a restaurant, consumers said price (60%) is the most important factor, followed by menu variety (54%), speed (25%), loyalty programs (10%) and online ordering options (7%).
Key Priorities for Businesses in 2025 Amid Restaurant Industry Inflation
Restaurants entering 2025 should focus on practical, guest-centered strategies that directly respond to ongoing inflationary pressures.
These priorities reflect the latest cost trends, consumer expectations and operational challenges:
- Redefining value: Emphasize portion control, quality ingredients and bundled deals that make price hikes feel justifiable to guests.
- Lean inventory and supply flexibility: Track real-time food costs and maintain flexible supplier relationships to adapt to commodity price swings.
- Smarter labor management: Use cross-training, shift optimization and scheduling software to control rising labor costs without cutting service quality.
- Menu engineering: Continuously review item performance to reduce complexity, increase margin per dish and align with available inventory.
- Digital loyalty and feedback loops: Focus on retaining price-sensitive guests through loyalty programs, targeted offers and mobile feedback that guide future decisions.
Restaurant Industry Inflation: Final Thoughts
Inflation has reshaped the restaurant industry from the ground up — driving up labor, rent, utility and supply costs while shifting how consumers spend and dine. Though price increases have slowed, operators are still navigating the financial aftershocks of the past five years.
In 2025, restaurants that succeed will be those that redefine value, manage labor smartly and adapt quickly to changing guest expectations.
Efficiency, affordability and targeted guest engagement will be key to staying competitive in an environment where cost pressures remain high and consumer habits continue to evolve.








Loading comments...